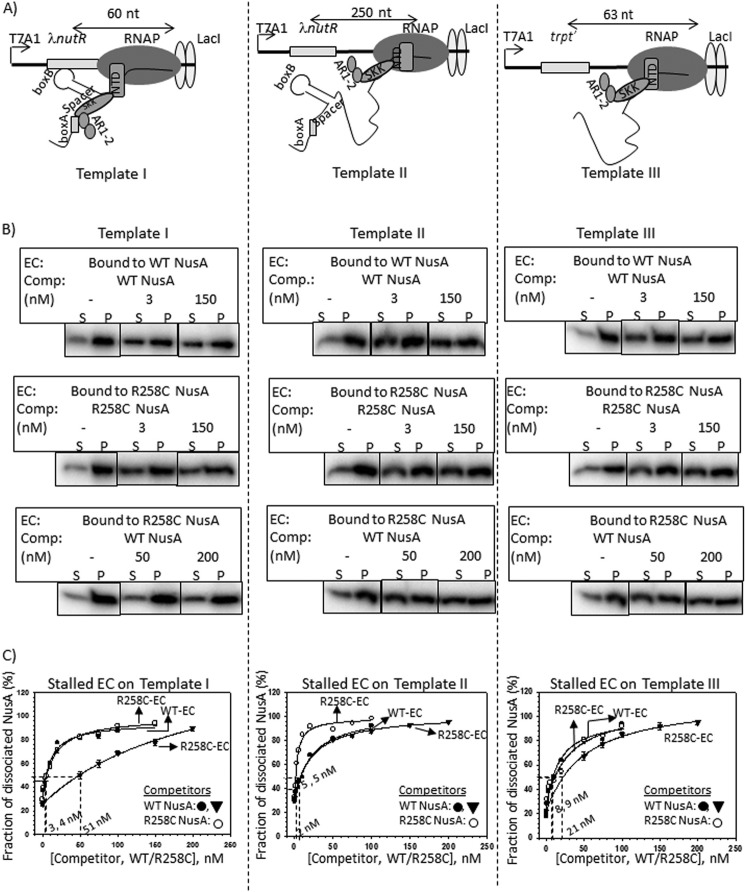
FIGURE 4.
Cold competition assays of radiolabeled NusA bound to stalled elongation complexes. A, schematics showing the stalled EC formed downstream of Rho-dependent terminators by the lac repressor (lacI). On templates I (left) and II (middle), ECs are stalled 60 and 250 nt downstream of the nut site of λ nutR, respectively. In template III (right), trpt′, lacking any nut site, is located 63 nt downstream of the terminator. All of the templates were immobilized to streptavidin-coated magnetic beads through a streptavidin-biotin bonding at their 5′-end. B, fractions of dissociated radiolabeled NusA ([32P]NusA) bound to the stalled EC on template I (left), template II (middle), and template III (right). Different derivatives of [32P]NusA bound to stalled ECs are indicated. C, plots obtained from the fraction of dissociated NusA in the presence of increasing concentrations of cold competitors, WT, and R258C NusA. Stalled ECs on template I (left), template II (middle) and template III (right) were bound to either WT (WT-EC) or R258C (R258C-EC) NusA. Data points were fitted to a hyperbolic equation. Concentrations of cold competitor corresponding to 50% change are indicated. In all of the experiments, S.D. values (error bars) were calculated from three independent experiments.