Fig. 1.
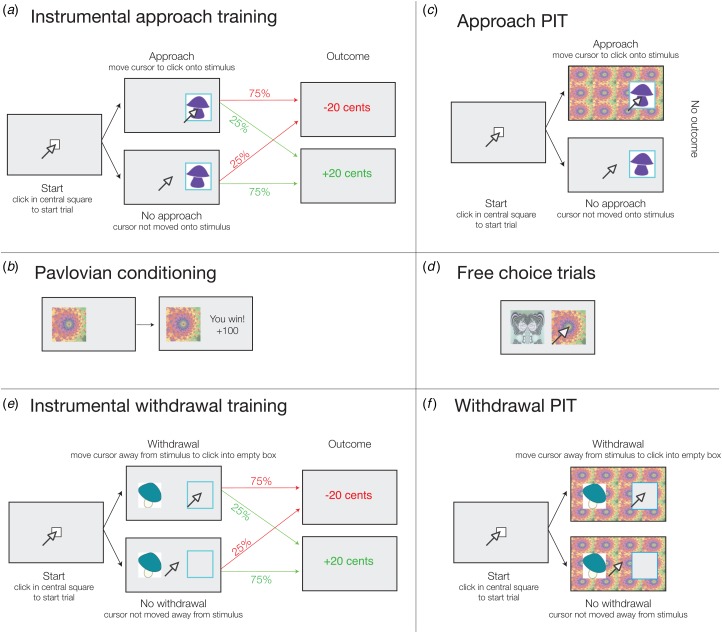
Task description. The task consisted of counterbalanced approach and withdrawal blocks, each subdivided into three parts: instrumental training, Pavlovian conditioning and Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT). (a) Instrumental approach training. Subjects started each trial by clicking inside a central square. Subjects were told they were collecting mushrooms in the woods and had to choose whether to move the cursor towards the mushroom (instrumental stimulus) and click inside the blue frame (approach go) to collect it, or not emit a response to not collect (approach no-go). Probabilistic outcomes (±20 cents) were presented immediately after go actions, or after a timeout period of 1.5 s had elapsed to define a no-go action. (b) Pavlovian conditioning. Subjects passively viewed fractal stimuli and heard auditory tones, deterministically followed after 1 s by wins and losses of 100, 10, 0, −10 or −100 cents for the best (henceforth labelled as ++), good (+), neutral (0), bad (–) and worst (– –) audiovisual Pavlovian conditioned stimuli (CSs), respectively. Tone frequency increased or decreased with CS value (counterbalanced). (c) Approach PIT stage. Subjects responded to mushrooms (instrumental stimuli) as before but now with fractals (Pavlovian CSs) tiling the background of the display and a tone corresponding to the fractal playing. No outcome was presented, but subjects were instructed to continue performing the instrumental task and that their choices counted towards the final total. No explicit instruction about the contribution of Pavlovian stimuli towards the final total was given. (d) To measure the acquisition of Pavlovian associations, passive Pavlovian conditioning trials (c) were interspersed with free choice trials administered on every fifth trial throughout Pavlovian conditioning (d). Here, subjects chose between two fractals presented concurrently. No outcome was presented, but subjects were told that the choices on these trials counted, with wins or losses added to the total provided at the end of the experiment. (e) Instrumental withdrawal training. As in approach training, except now subjects were told they were at home and had to throw away or not throw away mushrooms from their basket. They moved the cursor away from the mushroom and clicked in the empty blue frame to throw it away (withdrawal go) or did nothing to keep it (withdrawal no-go). (f) Withdrawal PIT. As in the approach PIT stage, the fractal stimuli tiled the background and subjects continued to perform the instrumental withdrawal task in extinction. For further details, see online Supplement S1. See online for the colour version of the figure.