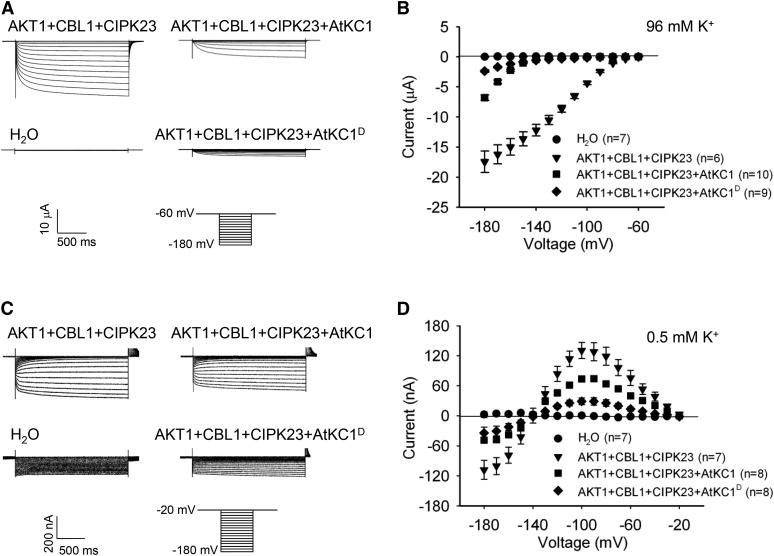
Figure 6.
AtKC1D strongly inhibits AKT1 conductance and restricts K+ leakage through AKT1 under LK conditions. A and C, Two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings in X. laevis oocytes. The oocytes were injected with distilled water as the control. The AKT1-expressing oocytes were injected with a RNA mixture of AKT1, CIPK23, and CBL1. The AKT1- and AtKC1 (or AtKC1D)-coexpressing oocytes were injected with a RNA mixture of AKT1, AtKC1 (or AtKC1D), CIPK23, and CBL1. The K+ concentrations in the bath solution were 96 mm (A) and 0.5 mm (C). The voltage protocols, as well as the time and current scale bars for the recordings, are shown. B and D, The current-voltage relationships of time-dependent steady-state K+ currents. The data were derived from the recordings shown in A and C, respectively. The instantaneous currents were subtracted using Clampfit software, and the time-dependent steady-state K+ currents were calculated for current-voltage curve plotting. Data are presented as means ± se.