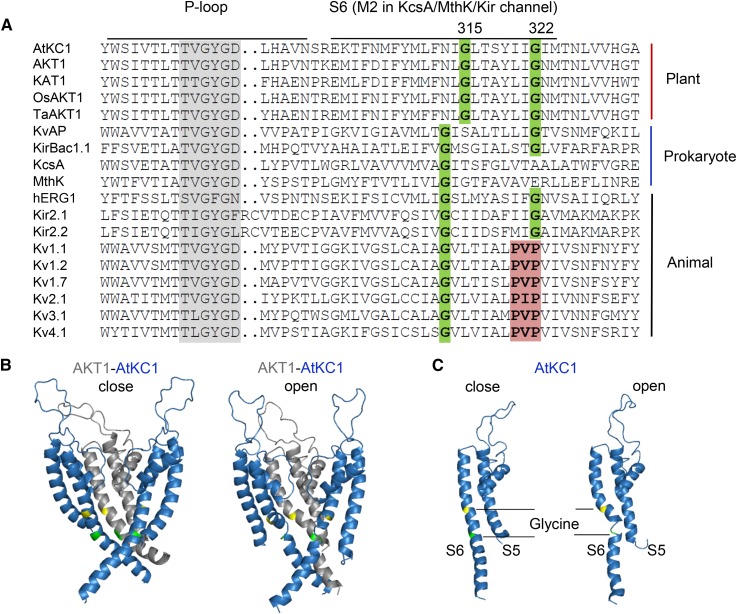
Figure 8.
Sequence alignment of K+ selective channels and structural prediction of the AKT1/AtKC1 heteromeric channel. A, Sequence alignment of S6 or M2 regions of K+ selective channels. Two conserved Gly residues (Gly-315 and Gly-322 in AtKC1) are highlighted in green. The PxP motif is labeled in red. Sequences are as follows: KvAP (GI:14601099; Aeropyrum pernix), KirBac1.1 (GI:33357899; Burkholderia pseudomallei), KcsA (GI:21225921; Streptomyces coelicolor), MthK (GI:499179590; Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus), hERG1/Kv11.1 (GI:4557729; Homo sapiens), Kir2.1 (GI:4504835; H. sapiens), Kir2.2 (GI:23110982; H. sapiens), Kv1.1 (GI:119395748; H. sapiens), Kv1.2 (GI:324021689; H. sapiens), Kv1.7 (GI:25952092; H. sapiens), Kv2.1 (GI:27436972; H. sapiens), Kv3.1 (GI:163792201; H. sapiens), and Kv4.1 (GI:27436981; H. sapiens). B, Structural prediction of the AKT1/AtKC1 heteromeric channel. The three subunits containing only the S5-P-S6 regions are shown for simplification. The three-dimensional structures of the closed (left) and open (right) states are shown. AKT1 and AtKC1 are labeled in gray and blue, respectively. The first conserved Gly residues (Gly-279 in AKT1 and Gly-315 in AtKC1) are highlighted in yellow, and the second conserved Gly residues (Gly-286 in AKT1 and Gly-322 in AtKC1) are highlighted in green. C, Three-dimensional structure of a single AtKC1 subunit.