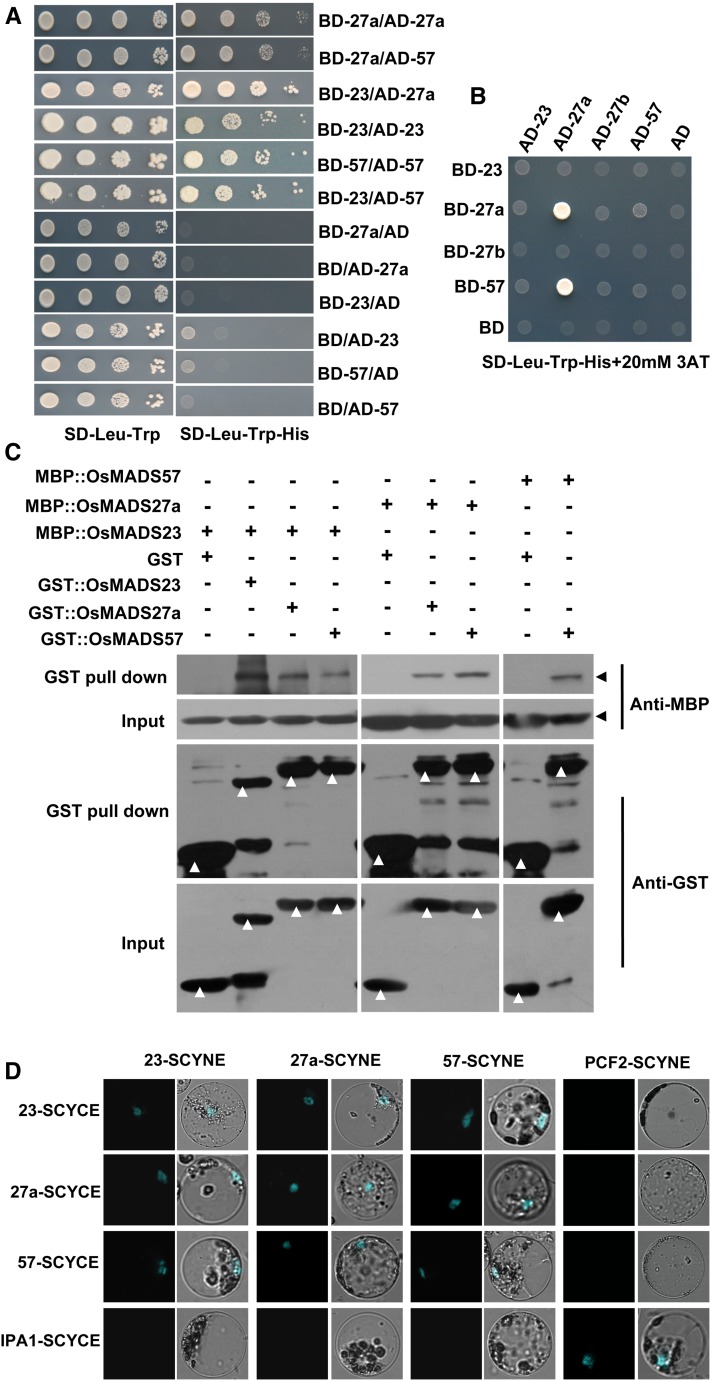
Figure 4.
Dimerization of OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57. A and B, Interaction patterns between OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57 in Y2H assays. The yeast AH109 stain was cotransformed with the indicated constructs and grown on selective synthetic dropout (SD) medium. The construct was labeled by the gene name after AD (GAL activation domain) or BD (GAL-binding domain). 3AT, 3-Amino-1,2,4-triazole. C, Interaction patterns between OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57 in GST pull-down assays. OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57 were fused with GST and maltose-binding protein (MBP) tags and applied for GST pull-down assays. The interactions between OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57 were detected by western blot using MBP antibody. Arrowheads indicate the expected bands of western blots. D, Interaction patterns between OsMADS23, OsMADS27a, and OsMADS57 in BiFC assays by cotransfecting rice protoplasts with the indicated constructs. Merged images of CFP fluorescence and rice protoplast are shown. The construct was labeled by the gene name followed by SCYNE (the N-terminal fragment of CFP) or SCYCE (the C-terminal fragment of CFP). The previously reported interacting proteins IPA1 (Ideal Plant Architecture1) and PCF2 (Proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene promoter binding factor 2) (Lu et al., 2013) were used as a positive control. The interactions between the three MADS proteins and IPA1 or PCF2 were detected and used as negative controls.