Figure 3.
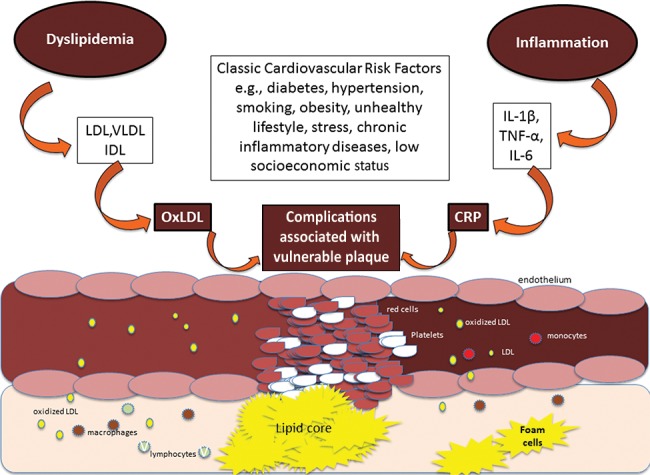
Increased cholesterol concentrations with oxidized lipoproteins and inflammatory stimuli through the release of cytokines with subsequent increase in C-reactive protein. Both pathways are related to classic risk factors and contribute to the development of and complications associated with vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. Thus, lipid and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein determinants provide additional information regarding cardiovascular risk. Strategies to control both mechanisms appear germane to decreasing the global cardiovascular disease burden, independent of ethnicity or geographic region.
