Figure 2.
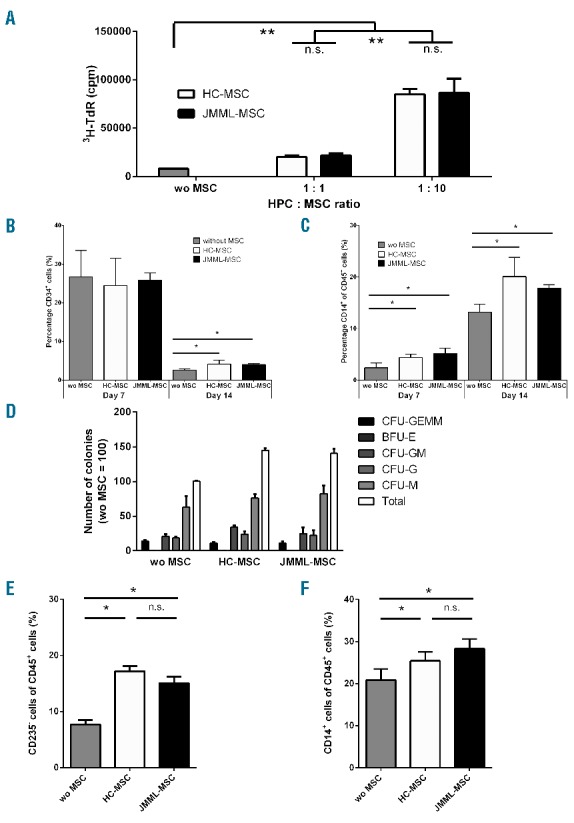
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia mesenchymal stromal cells (JMML-MSC) support the proliferation and differentiation of HPCs in vitro. (A). Both in the presence of JMML patient and healthy control (HC) derived MSCs the proliferation of CD34+ cells (HPCs) was increased after seven days of culture. MSCs alone did not show 3H-thymidine incorporation (data not shown). (B). HPCs lost the expression of CD34 after 14 days of culture; however, in the presence of MSCs (HPC : MSC ratio 1:5) the decline in CD34 expression was diminished. (C). HPCs acquired lineage markers, e.g. CD14, but no differences were seen between JMML-MSCs and HC-MSCs. (D). A significantly (P<0.05) increased number of colonies was seen in CFU-assays in the presence of MSCs (HPC : MSC ratio 1:60). (E and F). Cells harvested after colony formation contained increased percentages of CD235a negative and CD14 positive cells within the CD45+ cell population. Boxes indicate the mean, and error bars represent standard deviation. Experiments were performed with n=4 JMML-MSCs and n=2 HC-MSCs. Statistics were performed using Mann-Whitney tests: *P<0.05; **P<0.01; n.s.: non-significant.
