Figure 2.
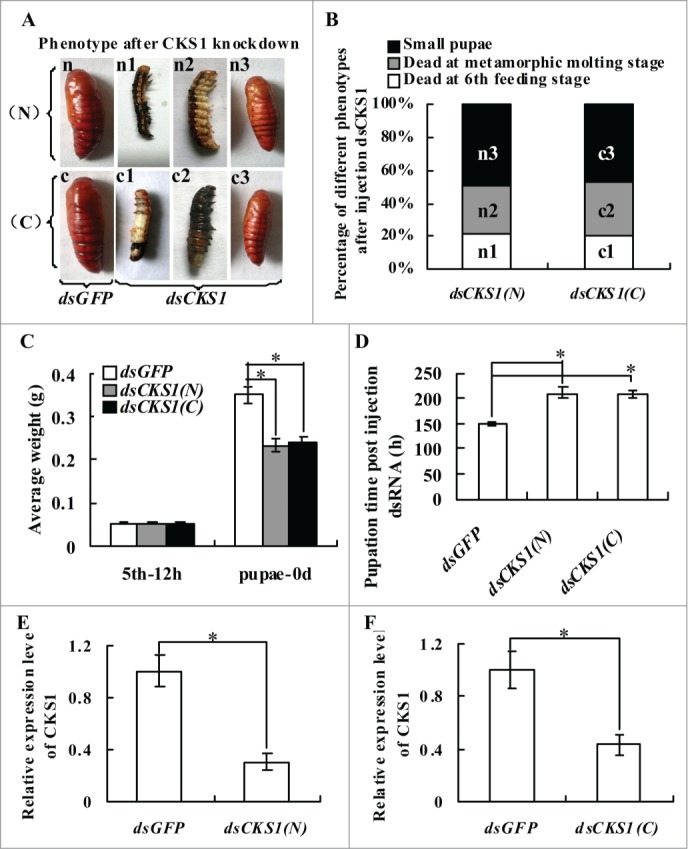
CKS1 knockdown blocks larval growth, delays pupation, and forms small-sized pupae. Insect phenotype after CKS1 knockdown by injecting non-overlapping dsCKS1 produced by N-terminus (N) and C-terminus (C), respectively, to fifth instar 12 h larvae (500 ng/larva, 3 times in 48 h interval). n and c: Larvae from control groups injected with the same quantity of dsGFP; n1 and c1: dead larvae at the sixth feeding stage; n2 and c2: dead larvae at the sixth metamorphic molting stage; n3 and c3, small-sized pupae; (B) percentage of distribution of different phenotypes in (A); (C) statistical analysis of average body weight of pupae after CKS1 knockdown by injecting dsCKS1(N) and dsCKS1(C), with dsGFP injection as the control; (D) statistical analysis of pupation time after dsRNA injection. (E and F), qRT-PCR analyzing the specificity of RNAi by dsCKS1(N) and dsCKS1(C), 24 h post dsRNA injection in 5th 12 h larval midgut. These experiments were repeated thrice (30 larvae × 3) and statistically analyzed. The asterisks indicate significant differences from the control group (P < 0.05) by using the student's t test.
