Figure 3.
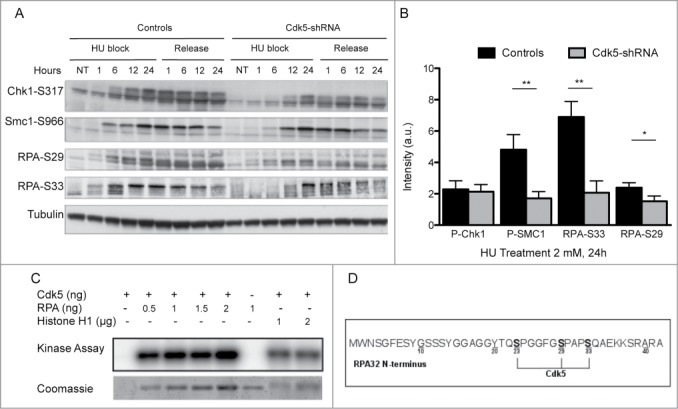
Decreased ATR and Cdks-dependent phosphorylation of Replication Protein A upon HU treatment in Cdk5 depleted cells. (A) Representative western blot analysis of phospho-SMC1-S966, phospho-Chk1-S317 and phospho-RPA-S29 and S33 in protein extracts from Control and Cdk5-shRNA cells during a 24 h HU block (2 mM) and over the following 24 h after release from the block. Total Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Quantification data are ratios of intensities of treated to non-treated cellular extracts after normalization with tubulin intensity, data are means ± SD from 2–3 independent experiments using 2 different HeLa Cdk5-shRNA clones have been calculated. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Unpaired t-test). (C) In vitro kinase assay showing the phosphorylation of purified RPA32 protein by Cdk5/p25 recombinant kinase after 30 min at 25° C. The image is representative of 3 independent experiments. The phosphorylation of histone H1 by Cdk5 was used as a positive control. (D) Sites of phosphorylation of the RPA protein by Cdk5 in vitro (same experimental settings as in 3C), identified by mass spectrometry: S23, S29 and S33. All three sites were detected in 7 independent experiments (full spectra are shown in Fig. S3).
