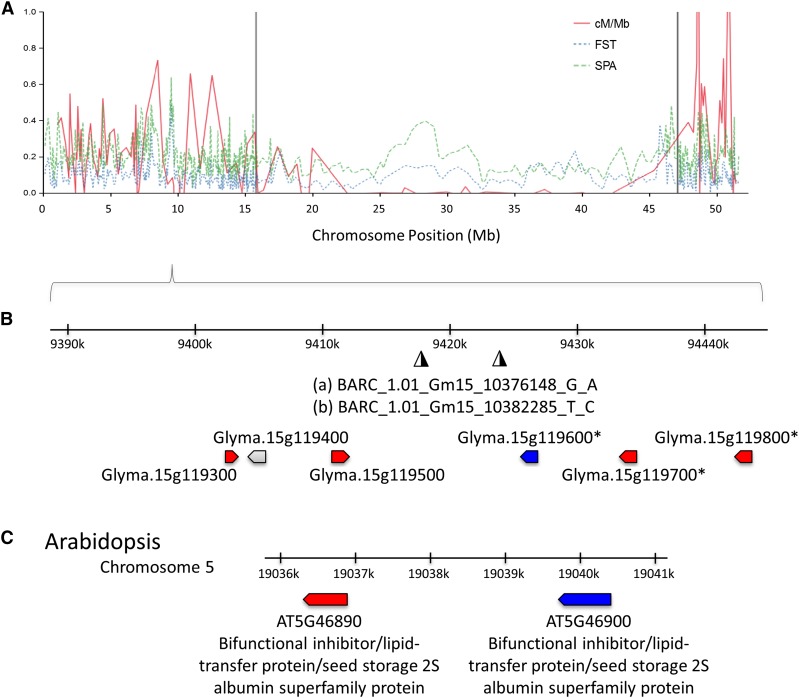
Figure 4.
SPA, FST, and recombination rate in the G. soja genome. (A) Sliding window of these values plotted on chromosome 15. Recombination decreases dramatically through the pericentromeric region, denoted by the vertical gray dotted lines. (B) Zoom in on 60 kb region around two significant SPA markers BARC_1.01_Gm15_10376148_G_A, and BARC_1.01_Gm15_10382285_T_C, a region of notably low recombination, and both high FST and SPA values. Three genes in this region (denoted with asterisks) were previously found to be duplicated, or deleted, in some elite soybean lines (Anderson et al. 2014). This cluster of genes appear to be members of a gene family. The Arabidopsis ortholog for the genes denoted in red is AT5G46890, a bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein. Similarly, the Arabidopsis ortholog for Glyma.15g119600, denoted in blue, is AT5G46900, a bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein. The implications of structural variation relating to FST, SPA hits, or recombination are not yet clear.