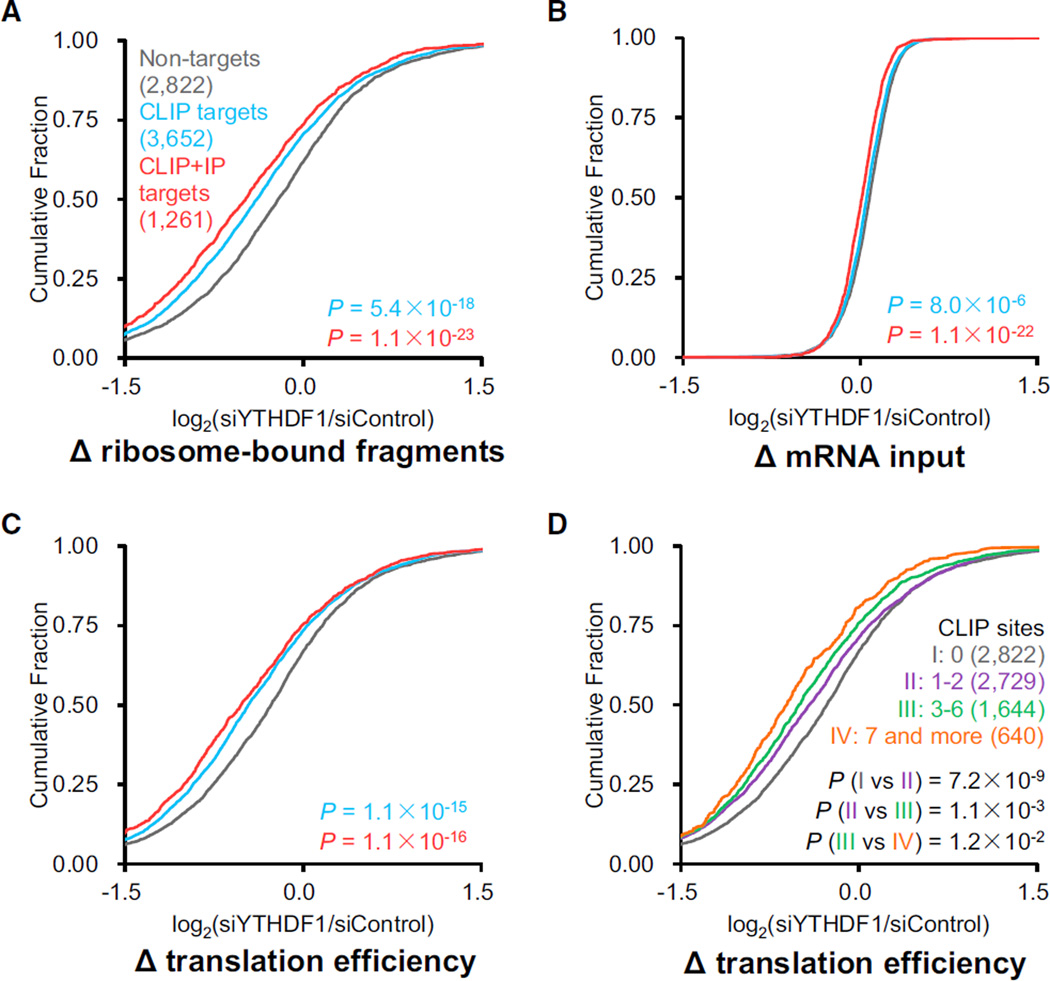
Figure 2. Knockdown of YTHDF1 Leads to Reduced Translation of Its mRNA Targets.
(A–C) Cumulative distribution log2-fold changes of ribosome-bound fragments (A), mRNA input (B), and translation efficiency (C, ratio of ribosome-bound fragments and mRNA input) between siYTHDF1 and siControl for non-targets (gray), PAR-CLIP-only targets (blue), and common targets of PAR-CLIP and RIP (red). p values were calculated using a two-sided Mann-Whitney test. (D) The mRNA lifetime log2-fold changes were further grouped and analyzed on the basis of the number of CLIP sites on each transcript. The extent of translation reduction caused by YTHDF1 knockdown correlates with the number of YTHDF1-binding sites for mRNA targets of YTHDF1. p values were calculated using a Kruskal-Wallis test.
See also Figure S2 and Table S1.