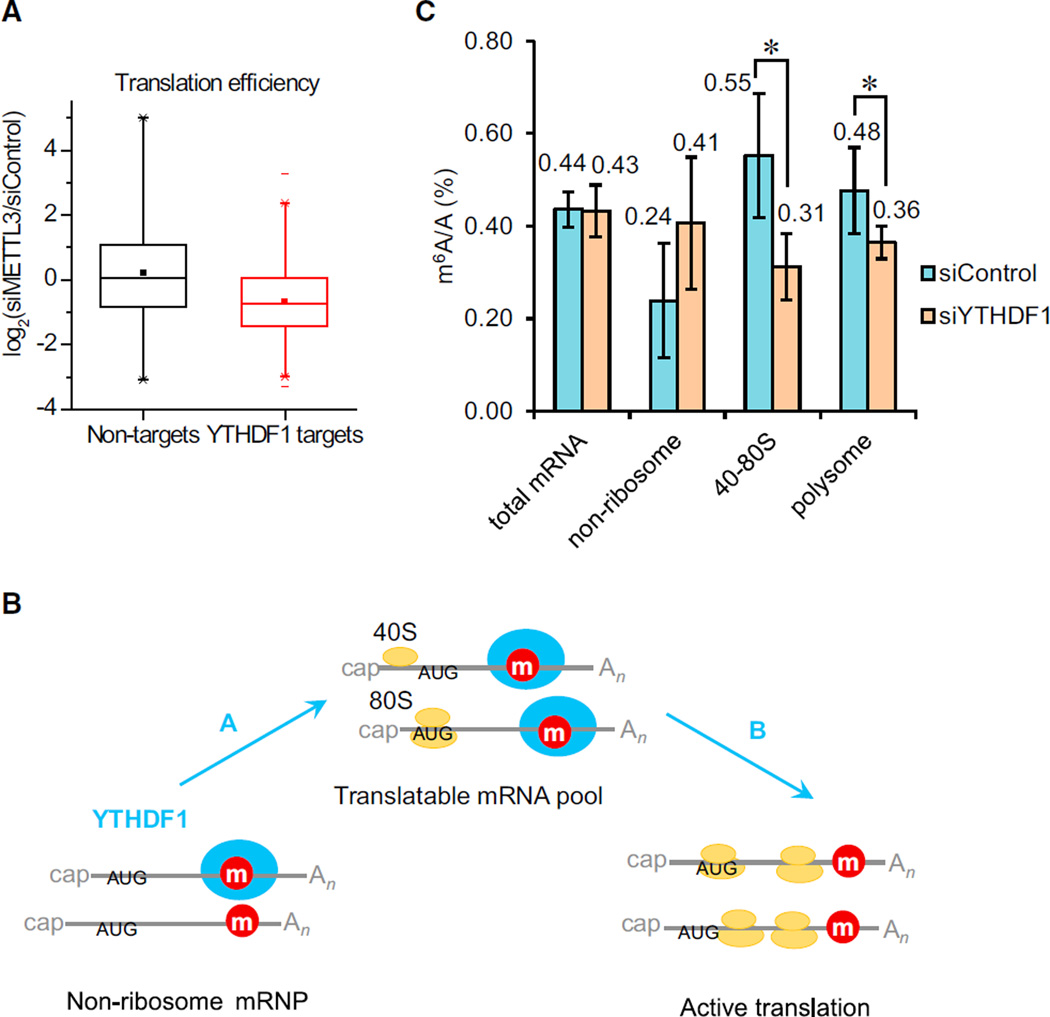
Figure 3. YTHDF1 Enhances the Translation of m6A-Modified RNAs.
(A) Knockdown of the m6A methyltransferase (METTL3) reduced the translation efficiency of YTHDF1 target transcripts. Cumulative distribution log2-fold changes of the translation efficiency between siMETTL3 and siControl for non-targets (black) and YTHDF1 RNA targets (red). p = 0, two-sided Mann-Whitney test.
(B) A diagram illustrating that YTHDF1 plays two potential roles in the translation of m6A-modified RNAs: in Role A, YTHDF1 shuttles more mRNAs to translation machinery; in Role B, YTHDF1 accelerates the translation initiation rate of methylated mRNAs.
(C) Quantification of them6A/A ratio of total mRNA, the non-ribosome portion, 40S–80S, and polysome determined by LC-MS/MS for the YTHDF1 knockdown samples compared to controls after 48 hr. p values were determined using a two-sided Student’s t test for paired samples. Error bars represent mean ± SD. For total mRNA, n = 8 (four biological replicates × two technical replicates), p = 0.71. For the rest, n = 5 (two biological replicates, two technical replicates + three technical replicates), p = 0.083, 0.035, 0.049 for nonribosome, 40S–80S, and polysome fractions, respectively.
See also Figure S3.