Figure 6.
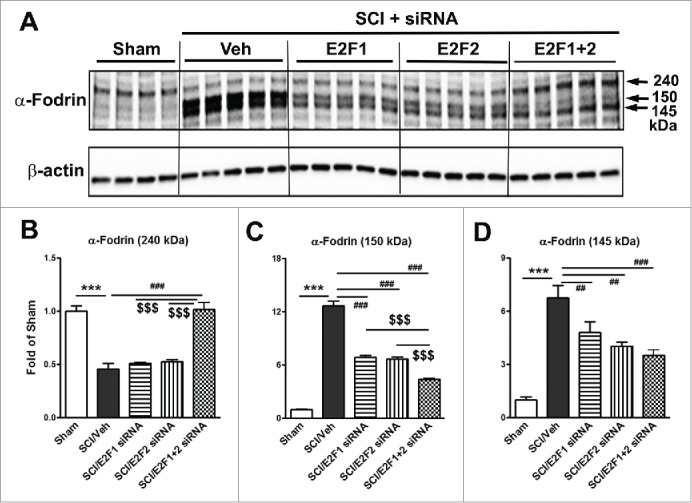
E2F1-2 siRNA reduces neuronal death at 24 h after SCI. E2F1, E2F2, E2F1+2, or scrambled siRNA were intrathecally administrated at 5 min post-injury and cleaved or uncleaved fragments of a-fodrin were assessed in the injured spinal cord at 24 h post-injury by Western blotting analysis. (A) Representative western blots for α-fodrin proteins and the loading control (β-actin). (B-D) Expression levels of α-fodrin (240, 150, 145 kDa) were normalized by β-actin, as estimated by optical density measurements and expressed as a fold of sham spinal cord. Quantitative analysis of western blots showed that 145 or 150 kDa cleavage fragment of the a-fodrin was increased 7- and 13- fold, respectively, whereas uncleaved fragment was decreased 60 %, as compared to sham-injury. These markers of apoptosis were significantly reversed by E2F1, E2F2, or E2F1+2 siRNA. Notably, E2F1+2 siRNA has greater effect than E2F1 or E2F2 single siRNA. n= 4-5 mice/group. ***p <0.001 vs. sham; ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 versus SCI/Veh; $$$p<0.001 vs. E2F1+2 siRNAs.
