Figure 1.
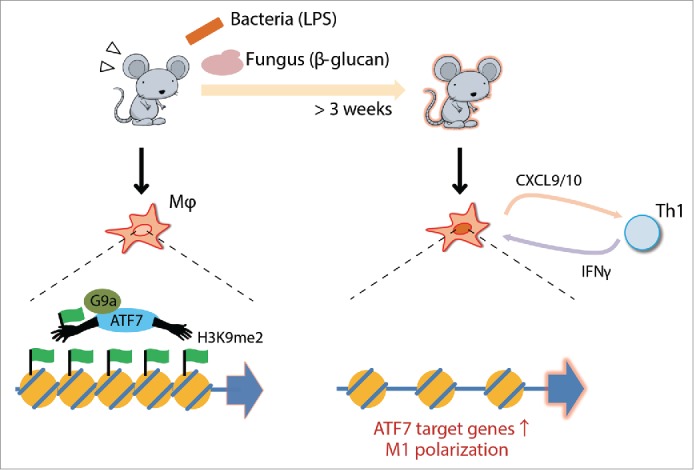
Schematic view of ATF7-mediated innate immune memory in macrophages. The ATF7-G9a complex forms heterochromatic structures by introducing H3K9me2. The complex is released from chromatin upon bacterial or fungal infection, thereby reducing the level of H3K9me2 and disrupting heterochromatin. Macrophages primed by infection express higher levels of ATF7 target genes, including M1 marker genes that affect Th1 activity.
