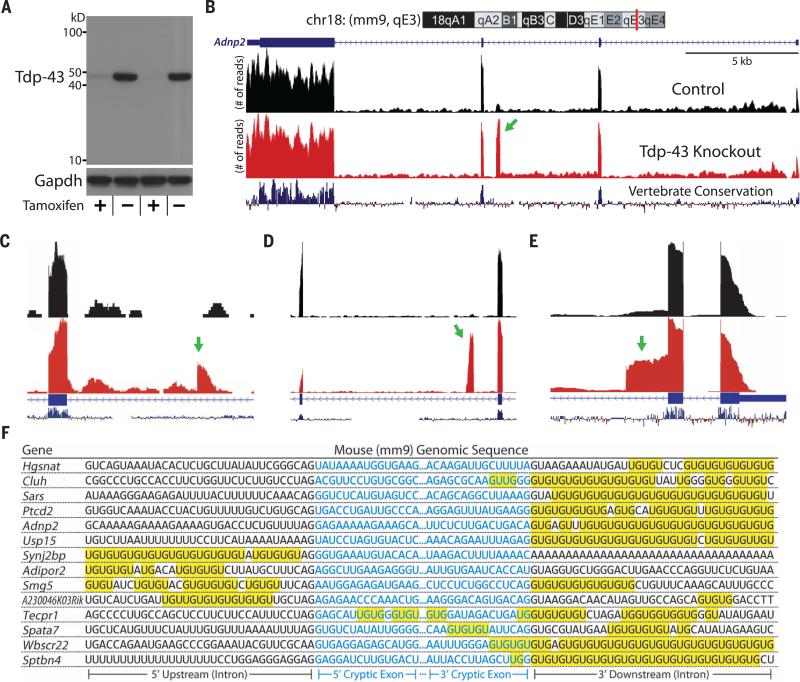
Fig. 1. Identification of Tdp-43–associated cryptic exons (Mus musculus).
(A) iTDPKO cells are depleted of Tdp-43 upon treatment with 4HT. (B) Visualization of the cryptic exon located in Adnp2 (red bar) of chromosome 18 (chr18) (top). Gene annotation is shown below, labeling exons (thick) and introns (thin). RNA-seq reads from iTDPKO untreated (“Control”) and 4HT treated (“Tdp-43 Knockout”) are aligned to the mm9 genome. The cryptic exon (green arrow) is not conserved (vertebrate conservation, bottom). Strand-specific analysis also confirms the incorporation of cryptic exons on the transcribing strand (fig. S11). (C to E) Most cryptic exons have standard 5′ and 3′ splice sites [Adipor2, (C)]. Occasionally, cryptic exons can present as transcriptional start sites [Sptbn4, (C)], polyadenylation sites [Synj2bp, (D)], or exon extensions [Wbscr22, (E)]. (F) Cryptic exons are flanked by UG tandem repeats that exist upstream, downstream, or internally.