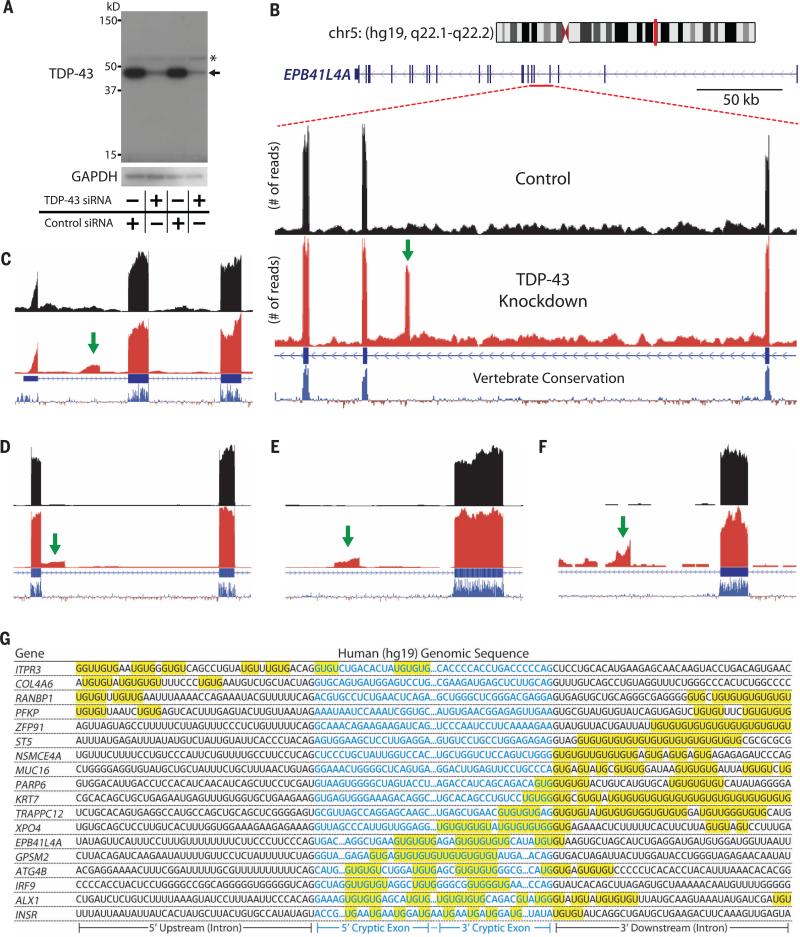
Fig. 3. Identification of TDP-43–associated cryptic exons (Homo sapiens).
(A) TDP-43 protein levels are greatly reduced when HeLa cells are treated with TDP-43 siRNA (asterisk indicates nonspecific band). (B) Visualization of the cryptic exon located in EPB41L4A. Zoom-in of gene annotation demonstrates that the cryptic exon (green arrow) resides in a nonconserved region. Strand-specific analysis also verifies the incorporation of cryptic exons on the transcribing strand (fig. S12). (C to F) IRF9 contains a transcriptional start site (C), KRT7 contains an exon extension (D), GPSM2 contains a standard cryptic exon (E), and INSR contains a polyadenylation site (F). (G) UG repeats are also found adjacent to human cryptic exons.