Figure 3.
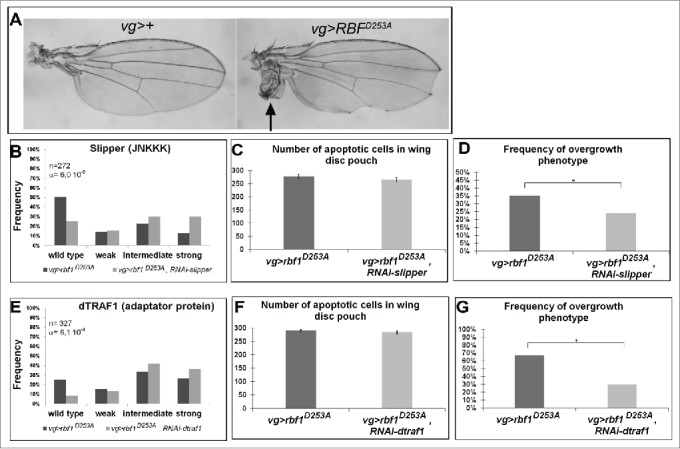
The kinase Slipper and the TNF associated factor dTRAF1 are required for rbf1D253A-induced overgrowth phenotypes but not for rbf1D253A-induced apoptosis. (A) Wild type wing and overgrowth wing phenotype observed in some fly expressing rbf1D253A (adapted from Milet et al. 2014).10 (B, E) Comparison of notch wing phenotypes distribution between vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+ and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/UAS-RNAi slipper (Wilcoxon test: n = 272, α = 6,0 10-06, Ws = 4,54) and between vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A /and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A /+; UAS-RNAi dtraf1/+ flies (Wilcoxon test: n = 327, α = 8,1 10-4, Ws = 3,34). (C, F) Comparison of apoptotic cells numbers in the wing pouch imaginal discs between vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+ and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A /UAS-RNAi slipper third instar larvae and between vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+ and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+; UAS-RNAi dtraf1/+ third instar larvae. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference between 2 genotypes (Student's test α < 0.05). For each genotype, quantifications were done for 30 third instar larval wing imaginal discs at least. (D, G) Frequencies of rbf1D253A-induced ectopic tissue observed in vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+ and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A /UAS-RNAi slipper flies and in vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+ and vg-Gal4, rbf1D253A/+; UAS-RNAi dtraf1/+ flies. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference between 2 genotypes (Chi2 test α < 0.05). Each experiment presented in B, D, E and G was independently performed 3 times.
