Fig. 1.
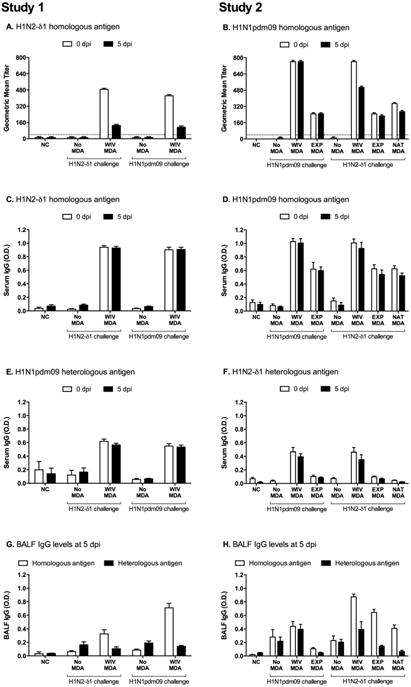
Serum and lung IAV-specific antibody levels due to maternally-derived antibodies (MDA) induced by vaccinating naïve dams with H1N2-δ1(1:7) WIV (Study 1) or boosting seropositive dams with H1N1pdm09 WIV or experimental infection (EXP) or from a non-boosted naturally exposed sow (NAT-MDA; Study 2). Reciprocal geometric mean HI titers against the homologous vaccine antigens are shown for 0 and 5 days post infection (dpi) for Study 1 (A) and Study 2 (B). Mean optical density (O.D.) in whole-virus ELISAs for serum IgG against H1N2-δ1 antigen (C, F) and H1N1pdm09 antigen (D, E). Treatments in Study 1 (A, C, E, G) were: pigs with no MDA or H1N2-δ1(1:7) WIV-MDA, challenged with homologous H1N2-δ1(1:7) or heterologous H1N1pdm09(2:6) virus. Treatments in Study 2 (B, D, F, H) were: pigs with no MDA, H1N1pdm09 WIV-MDA, H1N1pdm09 EXP-MDA, or H1N1pdm09 NAT-MDA challenged with homologous H1N1pdm09(2:6) or heterologous H1N2-δ1(1:7).
