Fig. (4).
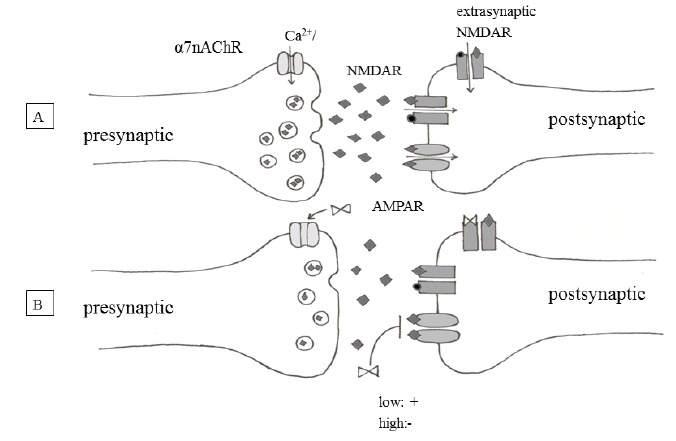
A: Normal conditions: After Ca2+ influx from the α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, the glutamate is releasing and binding to its receptors (extrasynaptic NMDAR, synaptic NMDAR, AMPAR) on the postsynaptic surface of the neurons. B: With kynurenic acid: After releasing into the perisynaptic area, KYNA exerts inhibition on extrasynaptic NMDARs and α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors ,while sparing synaptic NMDAR and AMPA receptor-mediated currents. In some articles it is mentioned that it has a Janus-faced impact on the AMPA receptors- e.g. it exerts a concentration-dependent dual effect. ♦ :glutamate, ●: glycin, ⋈ :Kynurenic acid.
