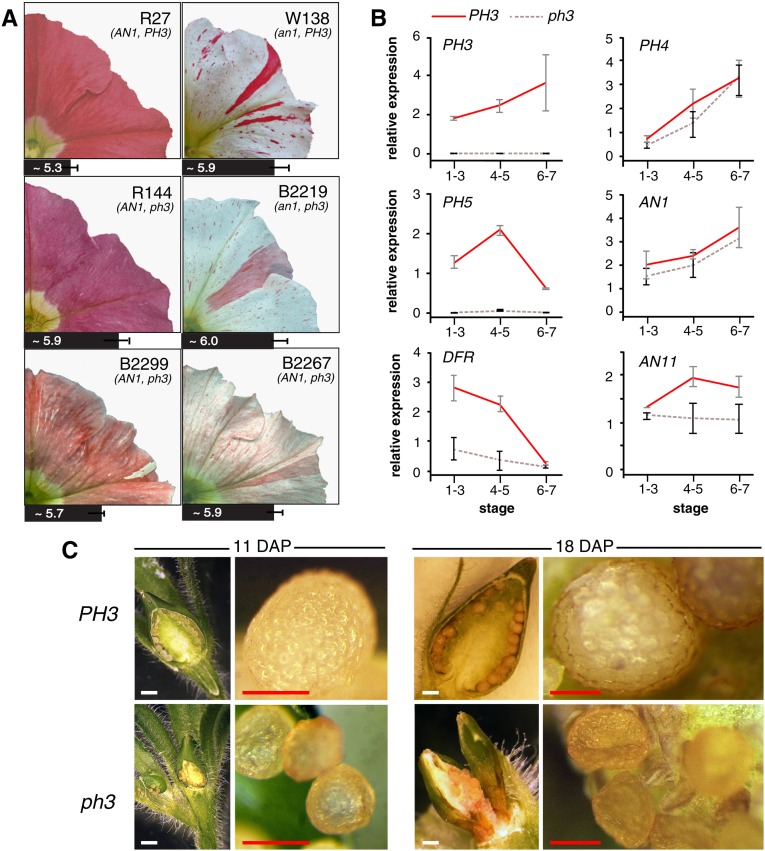
Figure 1.
Phenotype of ph3 Mutants.
(A) Petal limbs of the parental lines R27 (AN1+/+ PH3+/+) and W138 (an1m/m, PH3+/+), the derived stable recessive ph3 mutant R144 (AN1+/+ ph3V2068/V2068), and three transposon-tagged ph3 mutants B2267-1 (AN1+/m ph3V2068/B2267), B2219-1 (an1m/m ph3V2068/B2219), and B2299-1 (AN1m/Rev ph3V2068/B2299). The bars under the images represent the pH of the crude petal extract (n = 3, mean ± sd).
(B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of mRNA from PH3, the regulatory genes, PH4, AN1, and AN11, and the structural genes PH5 and DFR in petals of lines R27 (PH3+) and R144 (ph3) from flowers of developmental stages 1 to 3 (small bud and uncolored petals), 4 to 5 (fully expanded bud and colored petals), and 6 to 7 (fully opened flower with still closed anthers and flower with dehiscent anthers). Relative expression is indicated as the mean ± sd of three biological replicates.
(C) Seedpods of a PH3 and a ph3 mutant at 11 and 18 d after pollination (DAP). White bars = 1 mm, and red bars = 0.2 mm.