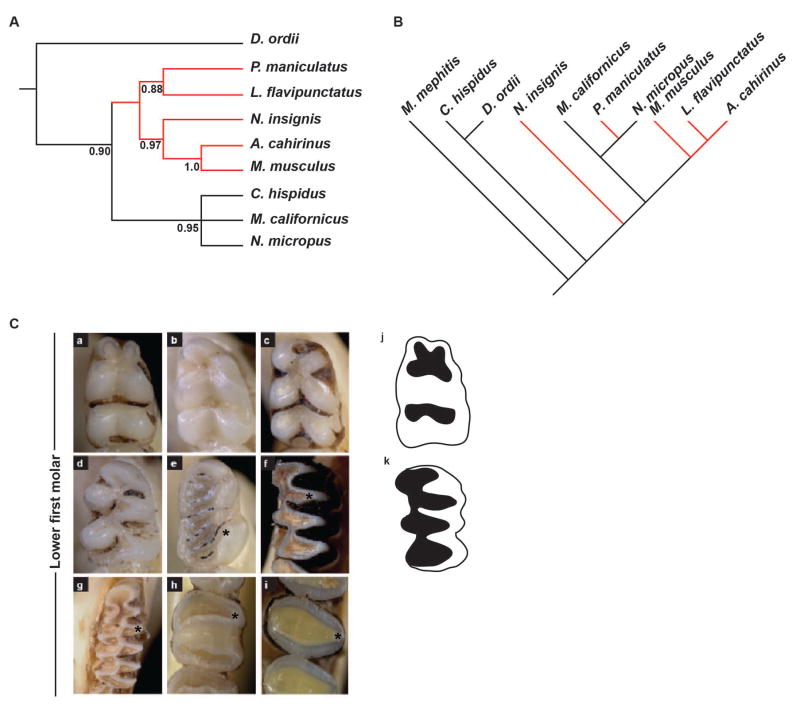
Figure 3.
Molecular phylogeny based on mitochondrial and Fgf9ECR1 sequence, and comparative anatomy based on lower first molar occlusal view. (A) Neighbor-joining tree based on Fgf9ECR1 sequence diversity depicts a single monophyletic clade (red branches). (B) Neighbor-joining tree modified from Fabre et al. 2012, depicting phylogenetic relationship based on mitochondrial DNA sequence among all examined species. (C) Occlusal view of lower first molar. Note triangular shape of the cusps in Microtus californicus and Neotoma microtus. a, Peromyscus maniculatus; b, Mus musculus; c, Lophuromys flavipunctatus; d, Acomys cahirinus; e, Napaeozapus insignis; f, Neotoma micropus; g, Microtus californicus; h, Chaetodipus hispidis; I, Dipodomys ordii; j, graphical representation of a rounded-cusp phenotype; k, graphical representation of a triangular-cusp phenotype.