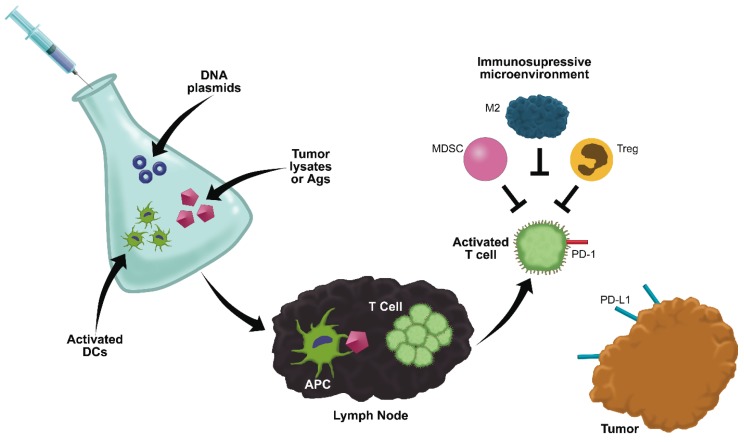
Figure 3.
Vaccination strategies and challenges. Vaccines utilize a variety of strategies to activate the immune system against tumor associated antigens (TAAs), including tumor cell lysates or peptide antigens, dendritic cells (DCs) activated with TAAs, and DNA plasmids designed to produce TAAs. The TAAs must then be presented by functional antigen presenting cells to T cells capable of recognizing the TAA. Once activated, T cells must traffic to the tumor and induce tumor cell death. T cell tolerance to TAAs, dysfunctional antigen presentation, T-cell exhaustion induced by checkpoint inhibitors (such as PD-1), and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment may all result in suppression of the immune response and variable patient responses to vaccination.