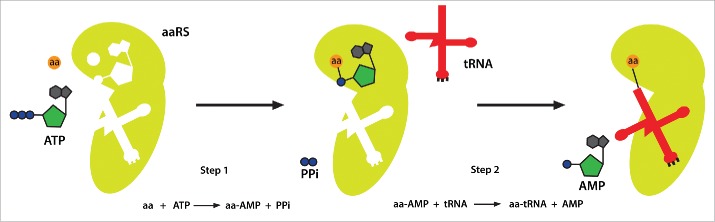
Figure 1.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase catalyzes a 2-step aminoacylation reaction. In the first step, the aaRS activates the substrate amino acid. By consuming an ATP it forms an aa-AMP intermediate. In the second step, the aa-AMP is transferred to the acceptor end of the cognate tRNA, generating an aa-tRNA that can be delivered to ribosomes for protein synthesis. aa, amino acid; aaRS, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; PPi, pyrophosphate.