Figure 3.
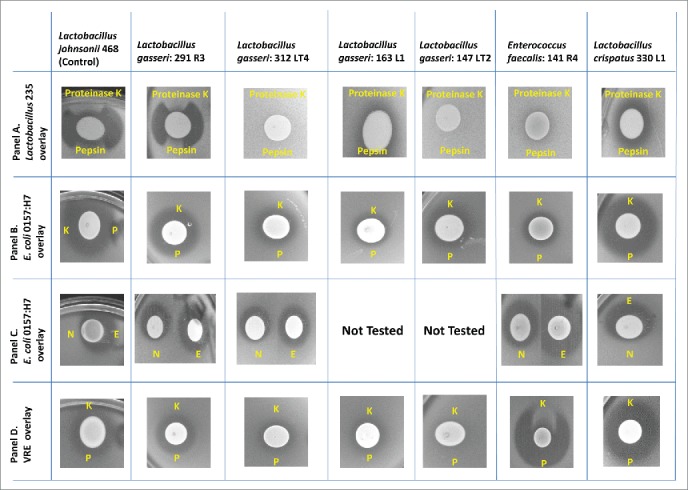
Bacteriocin screening. Only those isolates, pathogens and indicator combinations for which a zone of inhibition was observed are shown. All other combinations of isolate and pathogens did not result in a zone of inhibition in this spot-overlay detection method. Panels A & B: L. gasseri 291R3 produces a protease (Proteinase K (K) and Pepsin (P)) sensitive bacteriocin against the indicator L. delbeueckii 235, as indicated in Panel A. However, 291 R3's zone of inhibition against E. coli 0157:H7 is NOT sensitive to proteases. (Panel B). Further investigation was required to rule out acid production or an unusual bacteriocin structure. Panel C: Treatments: N- 10 N NaOH (3 μL) E- catalase (3 μL 10 mg/mL) Placing catalase in the zones had NO EFFECT; this ruled out hydrogen peroxide antimicrobial activity. But, placing 3 μL of 10 N NaOH inside the Zones of Inhibition (ZOI), diminished the antimicrobial activity by neutralizing the acid. Therefore, we conclude that the antimicrobial ZOIs against E. coli 0157:H7 are due to acid production. Panel D: The only isolate that produces a bacteriocin against a pathogen is E. faecalis 141 R4. This isolate produces a bacteriocin against Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus (VRE) and is sensitive to Proteinase K, but not Pepsin (P).
