Figure 5. In-silico modeling of PA with AMPK.
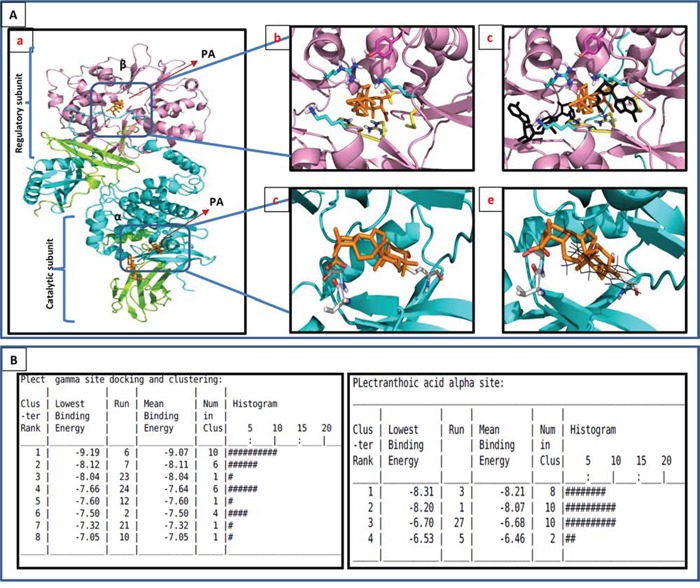
A. PA docked to AMPK by autodoc4. The model used was the AMPK structure with ligands in the PDB entry 4CFF (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4017, Nature Communications). α is cyan, β is green, γ is magenta and the ligands are gold. Ab. Docking results for the allosteric regulatory γ site. The ligand docks in a highly positive charged site. The nearest residues to the ligand are: Tyr121 (magenta), Arg70, Thr81, Met85, His151, Arg152. The carboxylate of PA is buried and interacts with Arg152. Ac. PA binds to the same regulatory site at which AMP (black) binds. Ad. Docking results for the α (kinase) binding site. The nearest residue are the backbone of Val24 at the carboxyl end, and Met93 at the -OH end. The primary interaction is hydrophobic. Ae. PA interferes with the binding site of staurosporine. B. Clustering data of PA to both α and γ subunits of AMPK.
