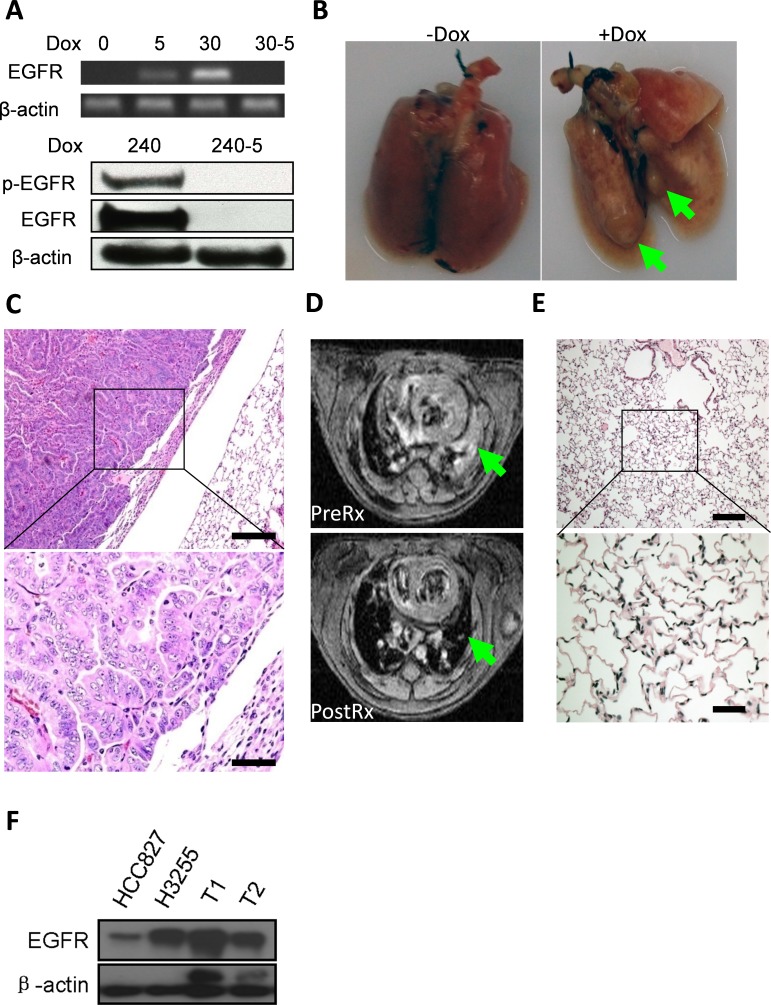
Figure 3. overexpression of wt-EGFR in lung epithelium is tumorigenic and necessary for tumor maintenance in vivo.
A. Wt-EGFR expression is tightly controlled in the transgenic mice. Upper panel for mRNA expression in the lung. Lower panel for protein expression in lung tissue before and 5 days after doxycycline withdrawal. All the gels were run under the same experimental conditions. Days for on doxycycline treatment are indicated by number. Withdrawal of doxycycline for 5 days is indicated by “-5”. B. Tumor nodules formed in lungs from CC10rtTA/TetO-wtEGFR bitransgenic mice. Left panel, mice not fed with doxycycline. Right panel, mice fed with doxycycline for around 8 months. Large tumor nodules highlighted with arrow-head. C. Tumors formed in CC10rtTA/TetO-wtEGFR bitransgenic mice are moderately to poorly differentiated lung adenocarcinoma. D. Tumors formed in CC10rtTA/TetO-wtEGFR bitransgenic mice depend on continuous expression of wt-EGFR for maintenance. upper panel: MRI images of mice after 8 months doxycycline induction (PreRx); lower panel: MRI images of same mice after doxycycline withdrawal (PostRx). Tumor region highlighted with green arrow-head. E. Histology of the lung of mice withdrawn doxycycline for 2 weeks. Histology (H&E staining) showed nearly normal lung, with occasional area of fibrosis. (scale bar for high magnification 50μm; scale bar for low magnification 200μm). F. TetO-wt-EGFR tumors express high amount of EGFR. Tumors from different mice (T1 & T2) were compared against HCC827 (EGFR exon19 deletion) and H3255 (EGFR L858R). Result showed mice tumors express high amount of EGFR.