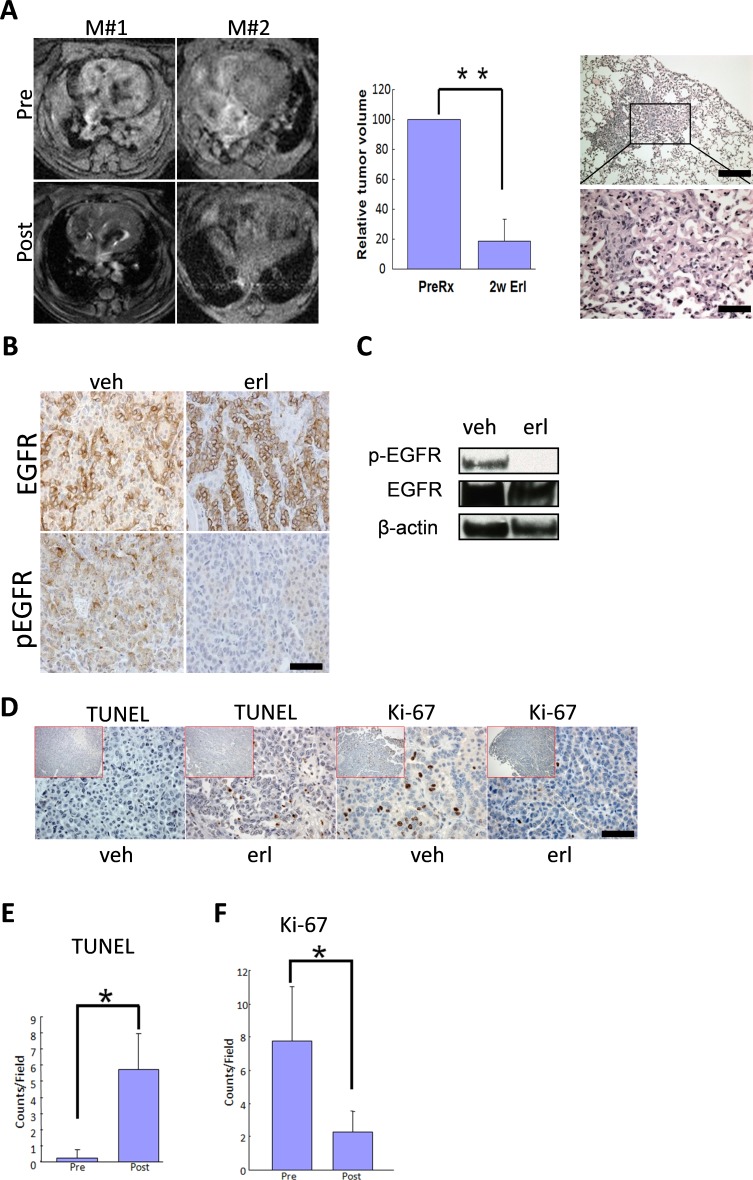
Figure 4. Lung cancers driven by wt-EGFR overexpression are sensitive to erlotinib treatment.
A. Tumor regression in CC10rtTA/TetO-wtEGFR mice in response to erlotinib treatment. Left panel: MRI images showing tumor regression of 2 representative mice (M#1 and M#2), Pre for before erlotinib treatment and Post for after erlotinib treatment; middle panel: quantification of tumor regression on 4 erlotinib treated mice; right panel. Histology of the lung in CC10rtTA/TetO-wtEGFR mice treated for 2 weeks. Lungs are nearly normal. Occasional areas of fibrosis are shown. B. wt-EGFR phosphorylation is sensitive to erlotinib treatment for 48 hours. IHC analysis of the lung tumors of mice treated with vehicle and erlotinib is shown. C. wt-EGFR phosphorylation is sensitive to erlotinib treatment for 48 hours. Western analysis of the lungs of mice treated with vehicle and erlotinib is shown. All the gels were run under the same experimental conditions. D. Erlotinib treatment resulted in arrest of proliferation and promotion of apoptosis in tumors. IHC staining shown for Ki-67 and TUNEL in the tumors from mice treated with vehicle and erlotinib. (scale bar 50 μm) E. Statistics of TUNEL staining. F. Statistics of Ki-67 staining.