Figure 4. RKIP inhibits cell migration and invasion by directly downregulating Notch1 activity.
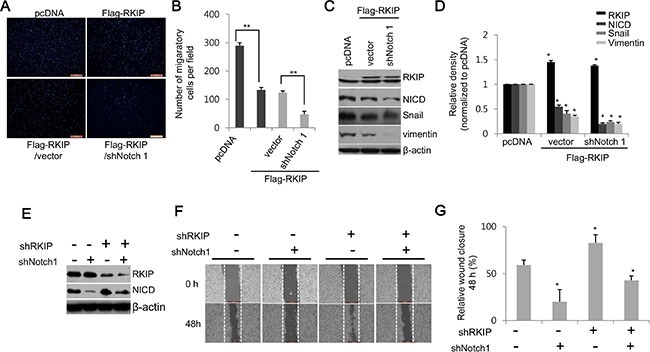
(A, B) Cell invasion of NICD-depleted, RKIP-overexpressing HeLa cells (FLAG-RKIP #5) was assessed via the Matrigel invasion chamber assay. (A) Photographs of propidium iodide-stained cells that invaded the chamber. (B) Quantification of the number of migratory cells in ten randomly selected fields. **p < 0.001. (C, D) Effect of Notch1 ablation on expression of EMT proteins in HeLa cells overexpressing RKIP. (C) Notch1 expression was knocked down by expressing the shNotch1 vector in RKIP-overexpressing HeLa cells (FLAG-RKIP #5), and total protein extracts (30 μg) were subjected to western blot analysis to examine the expression of the EMT markers, Snail and vimentin, in these cells. β-actin was used as loading control. (D) Relative expression levels of these proteins represented graphically. *p < 0.05. (E–G) Effect of Notch1 ablation on cell invasion in RKIP-overexpressing HeLa cells. Cell migration analysis of RKIP- and Notch1-knocked down H1299 cells. The expression of both RKIP and Notch1 was knocked down by co-transfecting the shRKIP- and shNotch1-expressing vectors in H1299 cells. (E) Expression of RKIP and NICD in these cells was determined by western blot analysis. (F) Migratory behaviors of these cells were evaluated using the wound-healing assay. (G) Cell migration quantified as described in Figure 3. Data indicate the mean ± S.D of the wound edge closure (%) of monolayer cells compared to controls (0 h). *p < 0.05. Scale bar, 500 μm.
