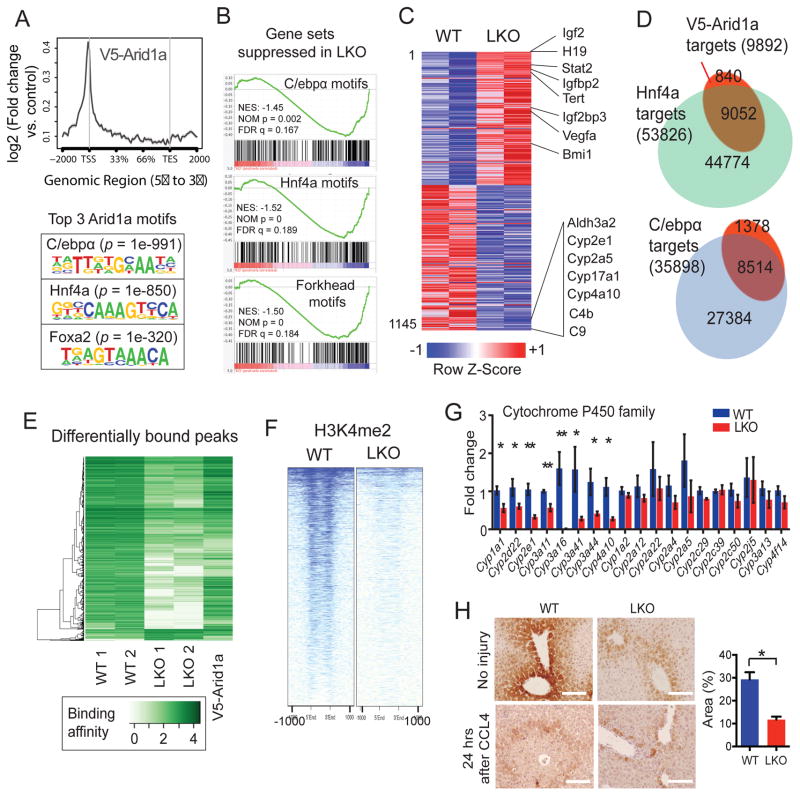
Figure 5. Arid1a-SWI/SNF complexes regulate tissue injury through chromatin remodeling.
(A) ChIP-seq in Arid1afV5/+ livers showed that V5-Arid1a binding is enriched at TSSs (top). Binding sites are associated with DNA sequence-specific motifs that overlap with C/ebpα, Hnf4a, and Foxa2 motifs (bottom).
(B) GSEA shows that Hnf4a, C/ebpα, Forkhead transcriptional target signatures are suppressed in LKO livers.
(C) Heat map of 1145 differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq (n = 2 and 2 livers, red is higher and blue is lower expression).
(D) 91% and 86% of V5-Arid1a binding peaks were also bound by Hnf4a and C/ebpα, respectively.
(E) Amongst the C/ebpα peaks identified in both WT and Arid1a LKO livers, 3952 showed significantly altered levels of C/ebpα binding and are depicted in this heat map (FDR <0.001, peaks are listed in Table S1). 95% of these sites were bound with less affinity in the LKO setting. Associated V5-Arid1a peaks are shown in the rightmost lane.
(F) ChIP-seq shows all H3K4me2 marks near peaks differentially bound by C/ebpα in WT and LKO livers.
(G) Cyp450 mRNA levels at baseline prior to injury in WT and LKO liver (n = 3 WT and 6 KO). This was performed in triplicates.
(H) Cyp2e1 immunostaining prior to and 24 hours after CCL4 injection. Scale bar = 100μm.
ImageJ quantification of Cyp2e1 positive area in an uninjured liver on the right. See also Figures S5 and S6 and Table S1.