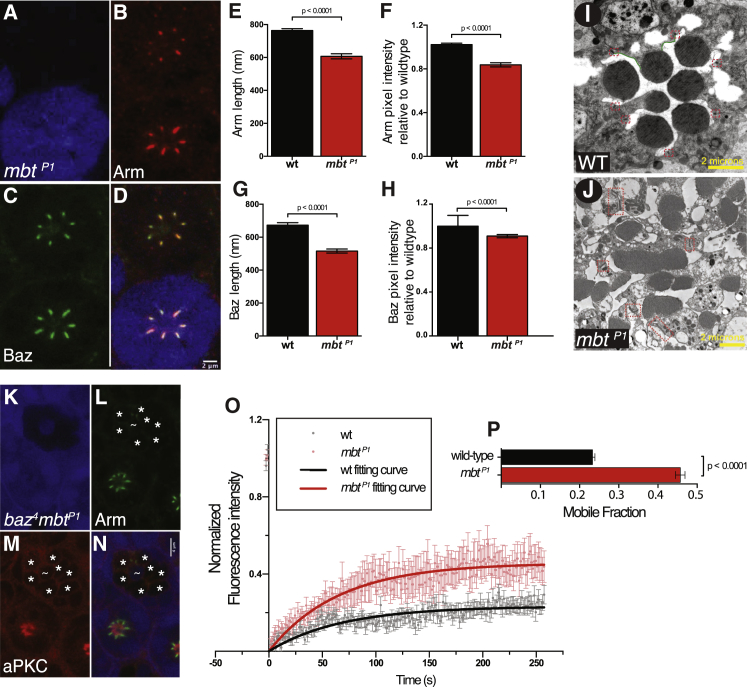
Figure 2.
mbt Promotes AJ Morphogenesis Independently from Baz
(A–D) mbtP1 mutant, lacking GFP (blue; A), Arm (red; B), Baz (green; C), and merge (D). The scale bars represent 2 microns.
(E) Mean length of Arm cortical domain in wild-type and mbtP1 mutants.
(F) Mean pixel intensity of Arm in wild-type and mbtP1. In (E) and (F), n = 202 (in four wild-type retinas) and n = 460 (in four mbtP1 retinas).
(G) Mean length of Baz cortical domain in wild-type and mbtP1 mutants.
(H) Mean pixel intensity of Baz in wild-type and mbtP1. In both (G) and (H), n = 99 (wild-type) and n = 107 (mbtP1), with measurements taken from five independent mbtP1 mosaic retina. In (E)–(H), columns represent mean and error bars represent the SEM of each dataset. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.
(I and J) Electron microscopy (I) on a wild-type ommatidium and (J) on the poorly developed apical membranes of an mbtP1 adult ommatidium. Ectopic AJ domains are boxed and sub-apical membranes in green. The scale bar represents 2 μm.
(K–N) baz4, mbtP1 mutant lacking GFP (blue; K), Arm (green; L), aPKC (red; M), and merge (N). Asterisks highlight mutant cells. A tilde marks a wild-type cell. The scale bars represent 4 μm.
(O) FRAP on E-cadherin::GFP in wild-type or mbtP1. Mean normalized fluorescence intensity in wild-type (gray; n = 18 from two individuals) and mbtP1 (pink; n = 15 from three individuals) is shown; error bars represent SEM. Fluorescence recovery curves of E-cad::GFP after photo-bleaching in wild-type (black) and mbtP1 (red) are shown.
(P) Mobile fraction of E-cadherin::GFP in a wild-type (black) or mbtP1 (red) background. The p value was calculated with an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test with Welch’s correction.