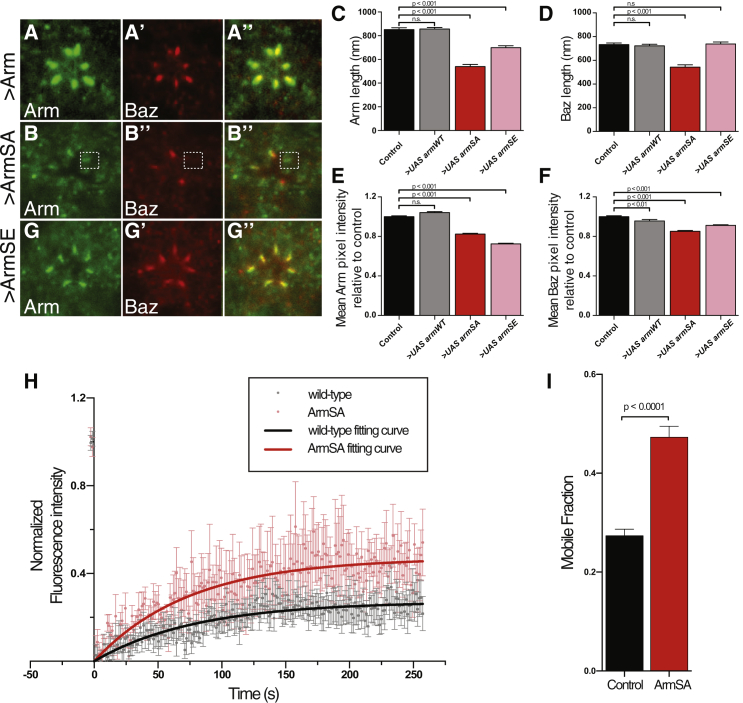
Figure 4.
Arm Phosphorylation Regulates AJ Material Stability during ZA Morphogenesis
(A) Overexpression of Arm::myc. Arm (green) and Baz (red) are shown.
(B) Overexpression of ArmSA561,688::myc. Arm (green) and Baz (red) are shown. A dashed rectangle highlights a ZA that contains Arm, but not Baz.
(C and D) Length of the Arm (C) and Baz (D) domains in wild-type and in photoreceptors expressing Arm::myc, ArmSA561,688::myc, or ArmSE561,688::myc.
(E and F) Mean pixel intensity for Arm (E) and Baz (F) measured relative to that of control photoreceptors. In (C)–(F), columns indicate the mean whereas error bars indicate the SEM (n > 200). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA and the Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison test for non-parametric samples.
(G–G”) Overexpression of ArmSE561,688::myc; Arm (green; G), Baz (red; G’), and merge (G’’).
(H) FRAP on E-cadherin::GFP in wild-type cells and in cells expressing ArmSA561,688::myc. Mean normalized fluorescence intensity in wild-type (gray; n = 14 from five individuals) and ArmSA561,688::myc (red; n = 9 from five individuals) is shown. Error bars represent SEM. Fluorescence recovery curves of E-cadherin::GFP after photo-bleaching in wild-type (black) and ArmSA561,688::myc (red) are shown.
(I) Mobile fraction of E-cadherin::GFP in a wild-type (black) or ArmSA561,688::myc (red) background. The p value was calculated with an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test with Welch’s correction.