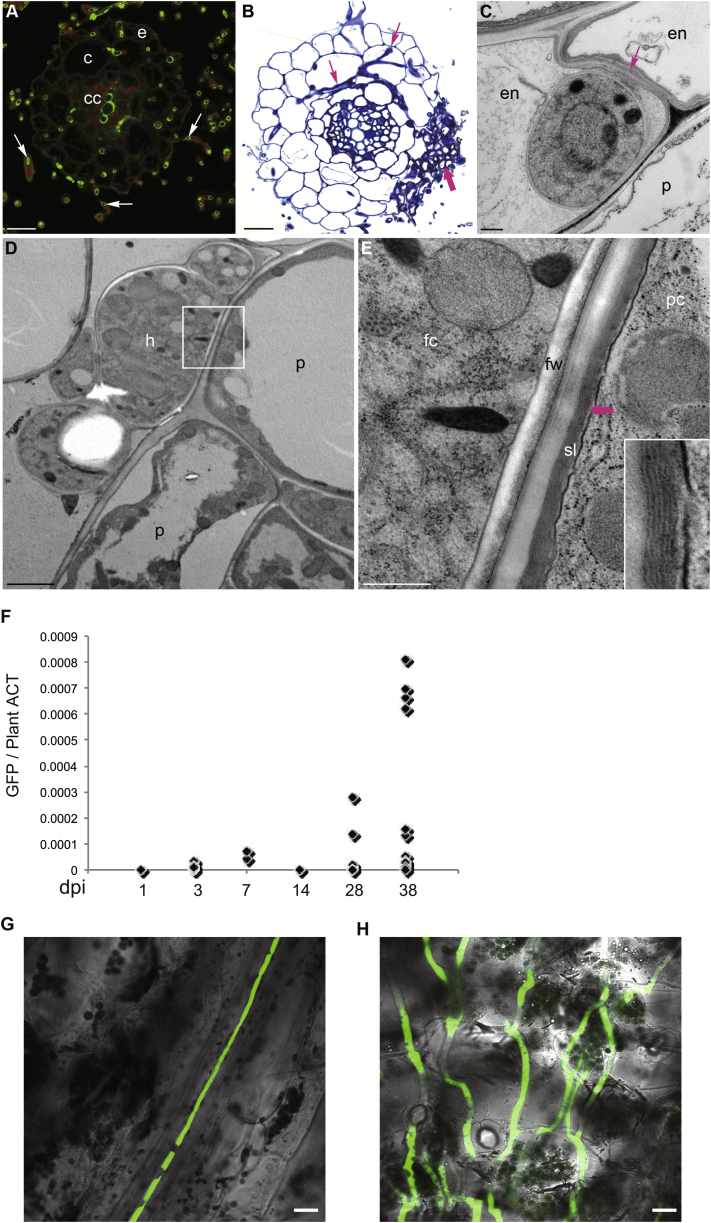
Figure S2.
C. tofieldiae Colonization of A. thaliana Roots and Systemic Colonization of A. thaliana Shoots, Related to Figure 2
(A) Epi-fluorescence micrograph of a root cross-section at 7 dpi. The section was stained with wheat germ lectin-FITC, which labels N-acetylglucosamine residues in fungal cell walls green, but also the secondary cell walls of xylem vessels in the central cylinder (cc). The root cortex (c), epidermis (e) and root hairs (arrows) are extensively colonized by intraradical hyphae, while abundant extraradical hyphae envelope the root at this stage.
(B) Bright-field micrograph of a root cross-section stained with Toluidine blue (7 dpi). Note the microsclerotium (thick arrows) developing in the epidermis and cortex and long intracellular hyphae spreading in the cortex (thin arrows).
(C–E) Transmission electron micrographs of ultrathin sections. (C) Cross-section of a hypha inside a root endodermal cell (en) as indicated by the presence of Casparian strip cell wall alterations in the anticlinal cell wall (arrow). 5 dpi. (D and E) Hypha (h) in contact with the root periderm (p) as indicated by the presence of layered suberin lamellae (sl) in the peridermal cell wall (arrow and inset). 7 dpi. fw, fungal wall; fc, fungal cytoplasm; pc, plant cytoplasm. Scale bars, 20 μm (A and B), 2 μm (D), 500 nm (C and E).
(F) Detection of C. tofieldiae (Ct) in healthy shoots of A. thaliana following root inoculation. A. thaliana Col-0 plants were grown hydroponically and the 20-day-old roots were infected with Ct-GFP spores. q-RT-PCR analysis with GFP-specific primers detected the presence of Ct-GFP in some healthy leaves. Approximately10 leaves per time point were collected.
(G) Confocal microscope image showing Ct-GFP hypha growing in vein tissue of a healthy leaf at 28 days post inoculation (dpi) of roots. Bar = 20 μm.
(H) Confocal microscope image showing Ct-GFP hyphae growing in a senescent leaf at 48 dpi. Bar = 20 μm.