Figure S3.
C. tofieldiae-Mediated Plant Growth Promotion in Phosphate Limiting Conditions, Related to Figure 3
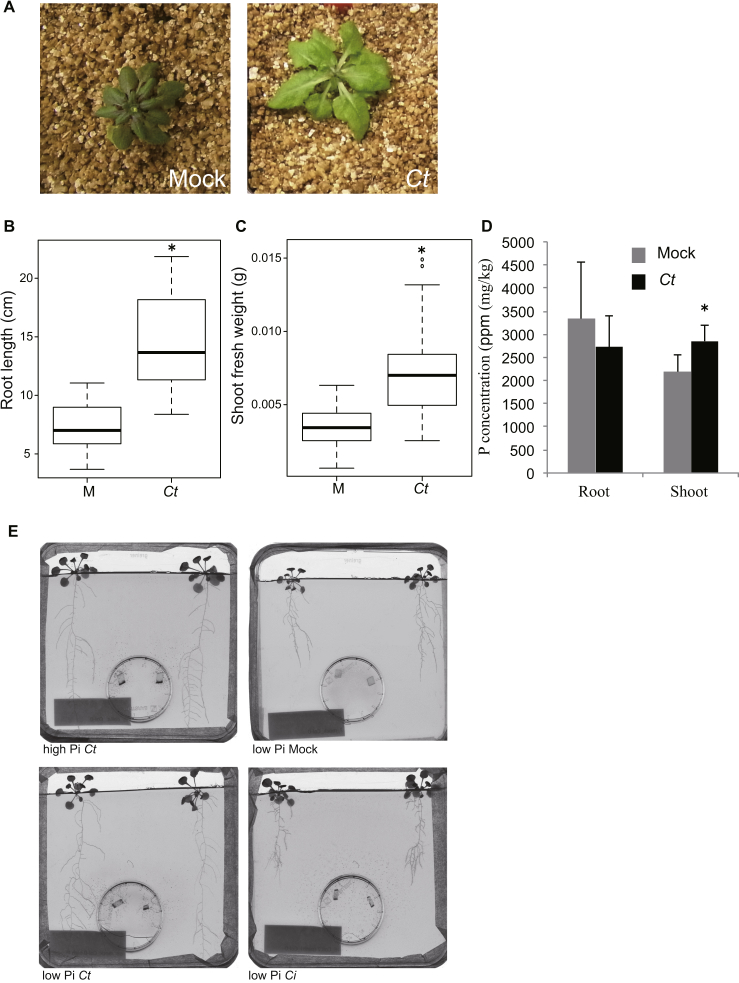
(A) A. thaliana vegetative growth in nutrient-poor vermiculite was improved in the presence of C. tofieldiae (Ct). Col-0 plants grown in half MS medium containing 0.8% sucrose were transferred to vermiculite soil either with or without the addition of Ct mycelium. The photographs were taken after co-cultivation for four weeks.
(B) Root growth promotion by Ct in low Pi conditions. Root length was measured 24 days after sterilized Col-0 seeds were inoculated with Ct spores (24 dpi). Ct treatment significantly increased root length (two-tailed t test, p < 0.0001). The graph represents combined data from three independent experiments.
(C) Shoot growth promotion by Ct when hydroxyapatite provided the sole Pi source. Shoot fresh weights were measured at 24 dpi. Ct treatment significantly increased the shoot fresh weight (two-tailed t test, p < 0.0001). The graph shows combined data from two independent experiments.
(D) The concentration of phosphorus (P) in A. thaliana shoots was significantly increased after growth in the presence of Ct. The P content of plants incubated with Ct for 24 days was measured by ICP-MS and was calculated in ppm based on the shoot dry weight. Ct treatment significantly increased the P content of shoots (two-tailed t test, p < 0.01). Similar results were obtained from one additional independent experiment.
(E) Illustration of the two-compartment co-cultivation system used for 33P translocation experiments. Seven-day-old A. thaliana seedlings were transferred to half MS agar medium providing either high or low Pi conditions in square (12 × 12 cm) Petri plates. Two agar plugs with or without C. tofieldiae mycelium were placed into the small circular Petri plates. After 7 days, 33P was added to the small plates, and the two-compartment system was further incubated for 17 days, when the photographs were taken and shoots harvested for scintillation counting.