Table 6.
GRADE Summary of findings table - secondary outcomes
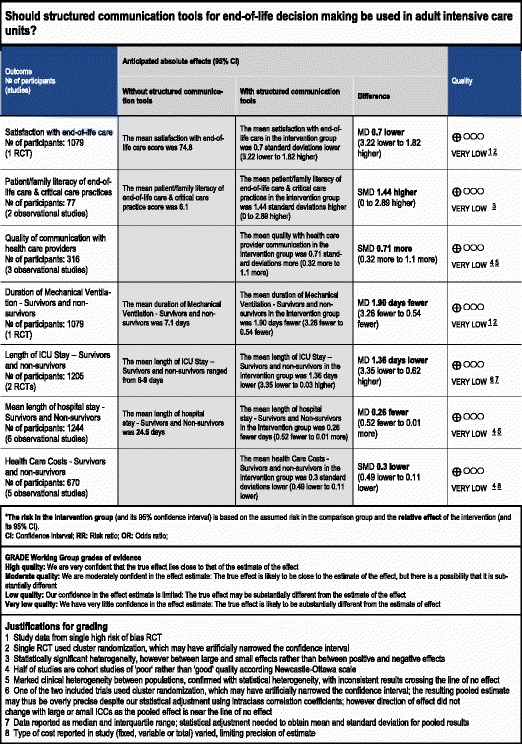
*The risk in the intervention group (and its 95 % confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95 % CI).
CI confidence interval, RR risk ratio, OR odds ratio, RCT randomized controlled trial, MD mean difference
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence
High quality: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect
Moderate quality: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate. The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different
Low quality: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited. The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect
Very low quality: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate. The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect
Justifications for grading
1. Study data from single RCT with high risk of bias
2. Single RCT used cluster randomization, which may have artificially narrowed the confidence interval
3. Statistically significant heterogeneity; however, between large and small effects rather than between positive and negative effects
4. Half of studies are cohort studies of poor rather than good quality according to the Newcastle-Ottawa scale
5. Marked clinical heterogeneity between populations, confirmed with statistical heterogeneity, with inconsistent results crossing the line of no effect
6. One of the two included trials used cluster randomization, which may have artificially narrowed the confidence interval; the resulting pooled estimate may thus be overly precise despite our statistical adjustment using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs); however, the direction of effect did not change with large or small ICCs as the pooled effect is near the line of no effect
7. Data reported as median and interquartile range; statistical adjustment needed to obtain mean and standard deviation for pooled results
8. Type of cost reported in study (fixed, variable or total) varied, limiting precision of estimate
