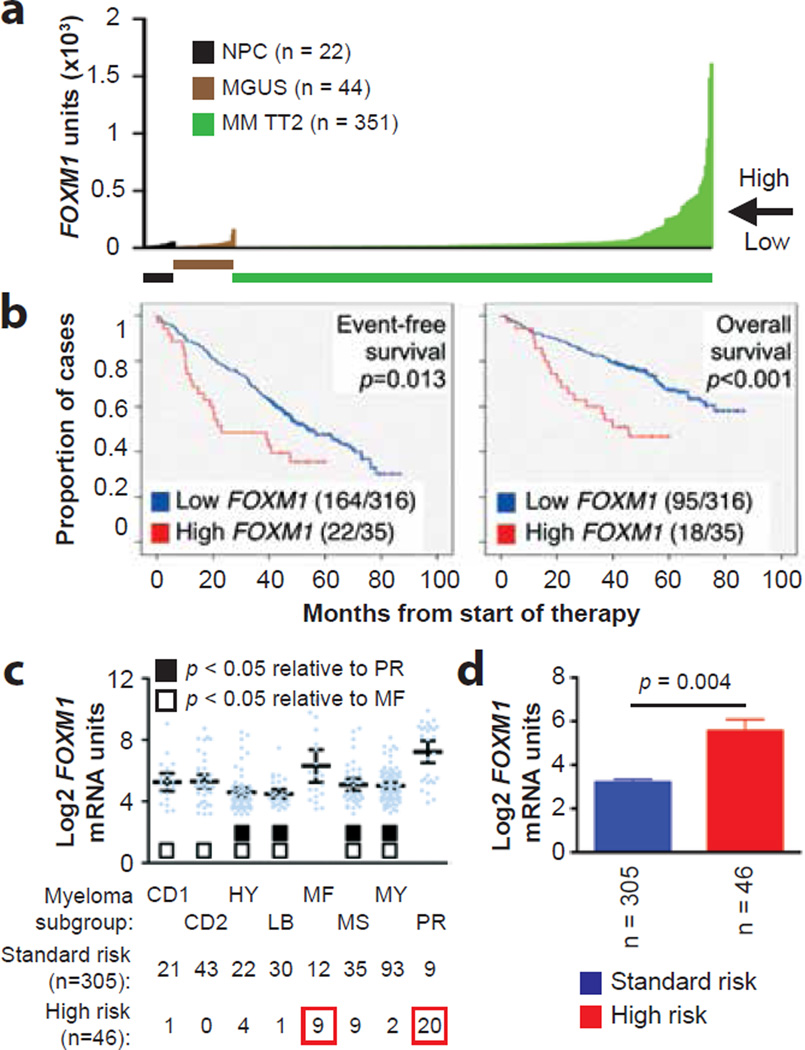
Figure 1. FOXM1 mRNA levels predict poor survival in a subset of patients with newly diagnosed myeloma.
(a) Line graph depicting the range of FOXM1 mRNA levels (gene probe ID 202580) in normal bone marrow (BM) plasma cells (NPC), “premalignant” BM plasma cells from individuals with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) or malignant plasma cells from patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) from the University of Arkansas Total Therapy 2 (TT2) cohort. Specimens exhibiting less and more than 200 units of FOXM1 message were categorized as FOXM1Low and FOXM1High, respectively. This is indicated by the horizontal, labeled arrow pointing left.
(b) Reduced event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) in newly diagnosed TT2 patients harboring high FOXM1 levels. Of 351 myeloma cases, 316 (90%) had low FOXM1 levels (blue curve) and 35 (10%) had high FOXM1 levels (red curve). EFS and OS data were available from 186 (53%) and 113 (32%) patients, respectively.
(c) Mean values of FOXM1 levels in 8 molecular subgroups of MM: CD1, CCND1/CCND3 group 1; CD2, CCND1/CCND3 group 2; HY, hyperdiploid; LB, low bone disease; MF, MAF/MAFB; MS, MMSET; MY, myeloid; PR, proliferation2. FOXM1 is significantly elevated in MF myelomas as compared to 6 subgroups with low FOXM1 levels (open squares), and in the PR myelomas as compared to 4 such subgroups (closed squares), as assessed using the Bonferoni t test. The number of patients within each molecular subgroup who exhibit the standard-risk or high-risk UAMS-70-gene signature is indicated at the bottom. In total, 46 of 351 patients fell into the high-risk category with at least one case in each of the molecular subgroups except CD2.
(d) FOXM1 expression in high-risk MM, as defined by the UAMS-70-gene signature (n = 46), is elevated compared to that in low-risk MM (n = 305; Mann-Whitney test).