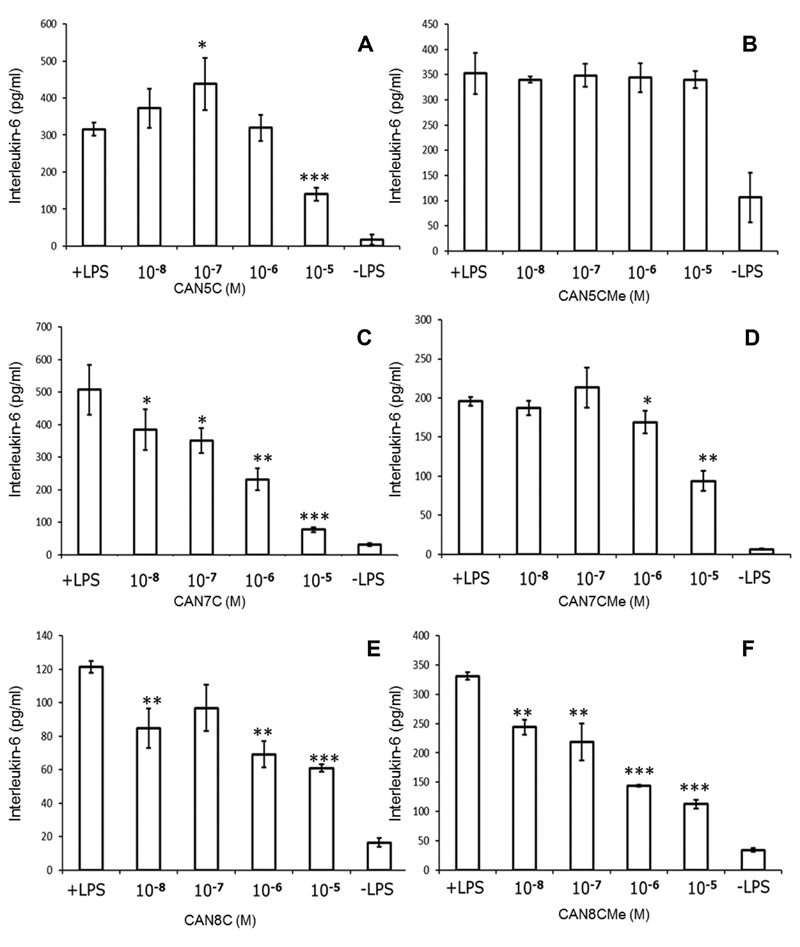
Figure 2.
Individual representative results from interleukin-6 release from cultured MG63 osteoblast-like cells (pg/ml) challenged with E. coli lipopolysaccharide (25 ng/mL: +LPS) and by LPS in the presence of the naphthoquinone compounds or without LPS or compound (-LPS) (mean ± SE for four replicates). (A) The 5-carbon carboxylic metabolite of vitamin K (CAN5C). (B) The methyl ester of the 5-carbon carboxylic metabolite (CAN5CMe). (C) The 7-carbon carboxylic metabolite of vitamin K (CAN7C). (D) The methyl ester of the 7-carbon carboxylic metabolite (CAN7CMe). (E) The aliphatic octyl carboxylic acid naphthoquinone (CAN8C). (F) The methyl ester of the octyl carboxylic acid naphthoquinone (CAN8CMe): *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001, all compound data were compared against the positive (+LPS) control.