Figure 1. CFH specifically binds to MDA modifications.
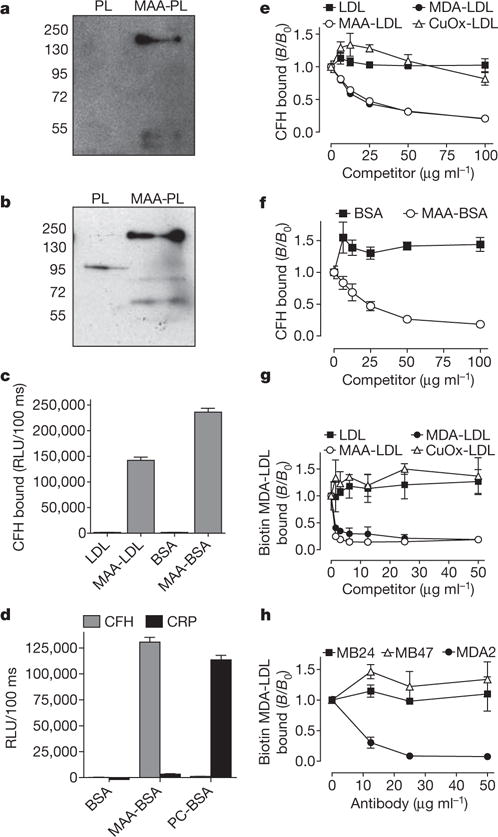
a, b, Immunoblot for CFH (molecular weight: 150 kDa) using eluates from either polylysine (PL) or MAA-polylysine (MAA-PL) beads incubated with Ldlr−/−Rag−/− mouse plasma (a) or human plasma (b). c, ELISA for binding of purified CFH (5 μg ml−1) to coated native LDL, MAA-LDL, BSA and MAA-BSA. Values are mean ± s.d. relative light units (RLU) per 100 ms of triplicate determinations. d, ELISA for binding of purified CFH or CRP (5 μg ml−1) to coated BSA, MAA-BSA and PC-BSA. Values are mean ± s.d. RLU per 100 ms of triplicate determinations. e–h, Competition immunoassays. e, f, Binding of purified CFH (e) or binding of plasma CFH (f) to coated MAA-BSA in the presence of increasing concentrations of LDL, MDA-LDL, MAA-LDL and Cu2+-oxidized (CuOx)-LDL, or BSA and MAA-BSA. g, Binding of biotinylated MDA-LDL to coated CFH in the presence of increasing concentrations of LDL, MDA-LDL, MAA-LDL and CuOx-LDL. h, Binding of biotinylated MDA-LDL to coated CFH in the presence of increasing concentrations of monoclonal antibodies specific for ApoB100 (MB24 and MB47) or MDA (MDA2). Data are expressed as a ratio of binding in the presence of competitor divided by the binding in the absence of competitor (B/B0) and represent the mean ± s.d. of triplicate determinations. As an estimate for the affinity, the dissociation constants Kd were calculated as 6.4 × 10−8 mol l−1 for the binding of CFH to coated MAA-BSA and 1.6 × 10−9 mol l−1 for the binding of MAA-BSA to coated CFH.
