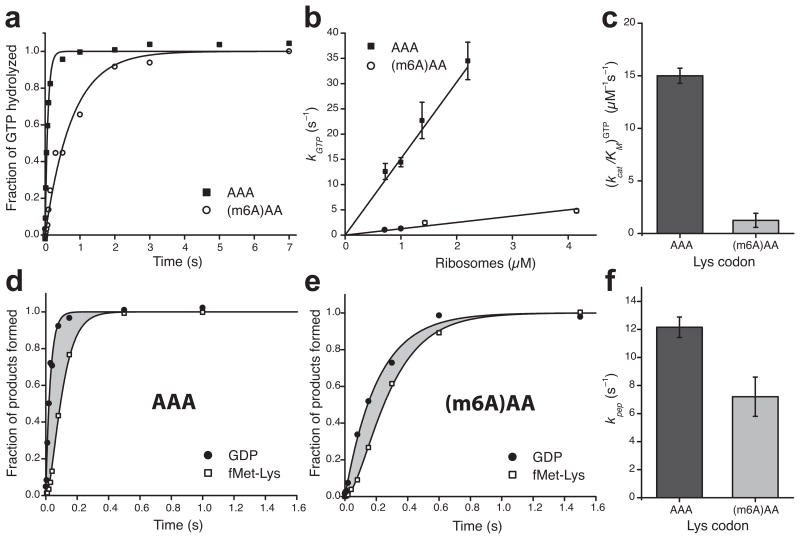
Figure 3.
Single-base m6A-modification slows down binding of ternary complexes to the A site of ribosomes during decoding and has minor effect on the subsequent steps. (a) Kinetics of GTP hydrolysis after binding of Lys-tRNALys ternary complexes (0.3 μM) to 70S (1 μM) initiation complexes programmed with AAA or (m6A)AA in the A site. (b) Dependence of the rate of GTP-hydrolysis, kGTP, on ribosome concentration. (c) Estimates of kcat/KM-values for GTP-hydrolysis from b. (d) and (e) Kinetics of GTP-hydrolysis and dipeptide fMet-Lys formation measured simultaneously in the same experiment. The grey areas represent the total time for all subsequent steps after GTP-hydrolysis up to and including peptidyl transfer. (f) Estimates of the compounded rate constant, kpep, for the steps after GTP-hydrolysis on EF-Tu up to and including peptidyl transfer, from experiments shown in d and e. See Supplementary Data Table 1 for data in c and f. Kinetic data in a, d and e are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars in b, c, and f represent s.d. (n = 3, technical replicates) as calculated from the fitting procedure32.