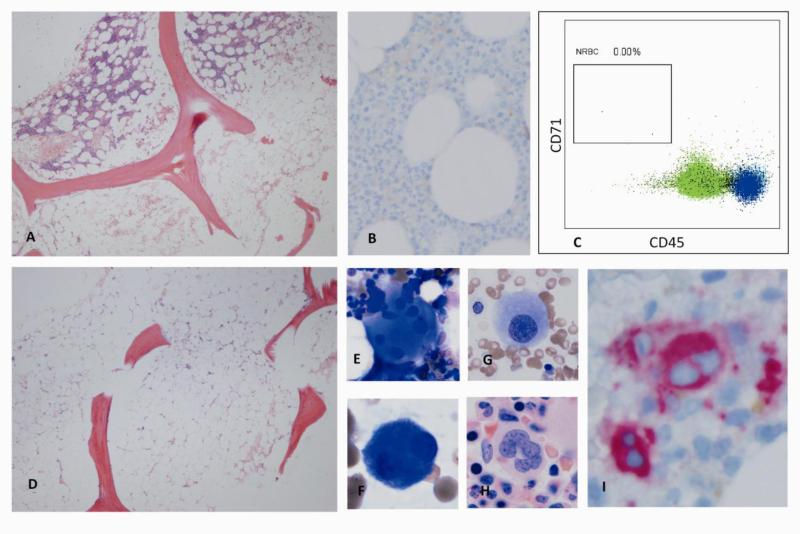
Figure 3.
A. Variably hypocellular marrow in aplastic anemia (cellularity <5% to 40%). B. Bone marrow biopsy of a patient with pure red cell aplasia (CD71 stain), revealing lack of erythroid precursors. C. Flow cytomery of bone marrow cells from a patient with pure red cell aplasia. Absence of erythroid lineage is confirmed and quantified. D. Typical bone marrow biopsy in severe aplastic anemia: hypocellular bone marrow replaced with fat. E-G. Examples of atypical megakaryocytes (E: Widely separated lobes without strand. F: small bilobated megakaryoctes. G: small monolobated megakaryocyte). H. Normal megakaryocte for comparison. I. Bone marrow biopsy of a patient with hypocellular MDS. Immunohistochemical staining for CD61 highlights atypical bilobated megakaryoctes. (Figure 3B-C: Courtesy of Dr. Raul Braylan)