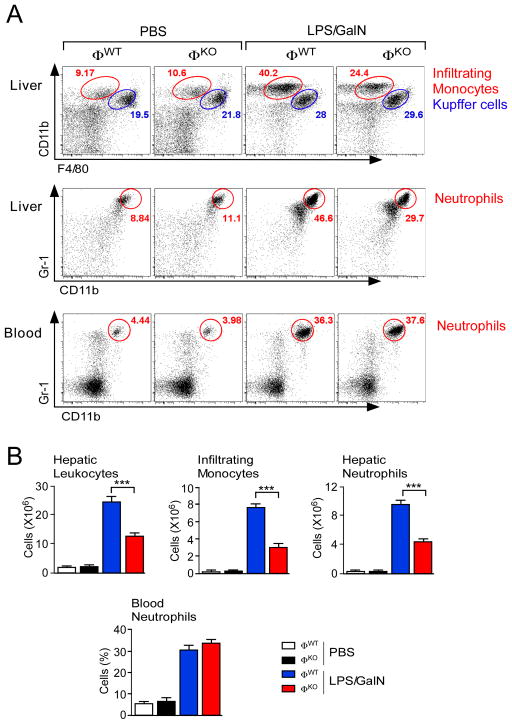
Figure 1. Myeloid JNK promotes hepatic infiltration by monocytes and neutrophils.
(A) Mice (ØWT and ØKO) were treated with PBS or LPS/GalN (5.5 h). Representative flow cytometry data of hepatic leukocytes stained with antibodies to CD11b and F4/80 (red, infiltrating monocytes; blue, Kupffer cells) are presented (upper panels). Representative flow cytometry data of neutrophils stained with antibodies to CD11b and Gr-1 (red) within total hepatic leukocytes (middle panels) and blood (lower panels) are presented.
(B) The total number of hepatic leukocytes is presented (mean ± SEM; PBS ØWT, n = 3; PBS ØKO, n = 4; LPS/GalN ØWT, n = 13; LPS/GalN ØKO, n = 12). The number of total hepatic leukocytes corresponding to infiltrating monocytes, infiltrating neutrophils, and Kupffer cells is presented (mean ± SEM; PBS ØWT, n = 5; PBS ØKO, n = 6; LPS/GalN ØWT, n = 11 (except neutrophils, n = 16); LPS/GalN ØKO, n = 11 (except neutrophils, n = 15)). The percentage of total blood leukocytes corresponding to neutrophils is also presented (mean ± SEM). PBS groups, n = 3; LPS/GalN groups, n = 9). Statistically significant differences between ØWT and ØKO mice are indicated (***, p<0.001).
See also Figure S1.