FIGURE 4.
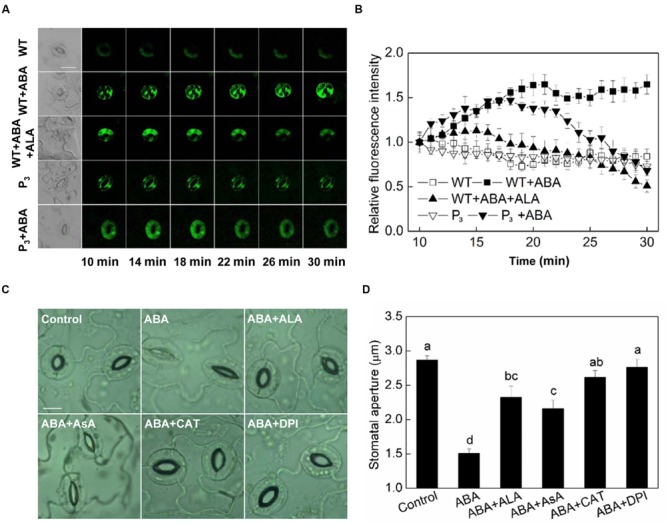
ALA reduces ABA-induced H2O2 accumulation in guard cells. (A,B) Changes in H2O2 content in guard cells. Isolated epidermal peels of pre-illuminated wild-type and YHem1 transgenic (P3) Arabidopsis were loaded with H2DCF-DA for 30 min in darkness at 25°C, then excess dye was removed for the following treatments. Wild-type peels were transferred to either the opening buffer alone or supplemented with 10 μM ABA, 10 μM ABA + 0.5 mg L-1 ALA, and P3 peels were transferred to either the opening buffer alone or supplemented with 10 μM ABA. Five minutes later, fluorescence of the above-treated peels (A) was observed using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica TCS SP8 STED 3X, LSCM) and Time-course and Photoshop software. For each treatment, the first picture is bright field image and the following are fluorescence images corresponding to the bright field image at 1 min intervals. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Time course changes of the relative fluorescence in guard cells of each treatment. Data are normalized by calculating the relative changes in fluorescence over initial values. Values are the means of 15 measurements ± SE from three independent experiments. (C,D) The inhibitive effect of ALA on ABA-induced stomatal closure is similar to AsA, CAT, and DPI, all of which inhibit ABA-induced stomatal closure via decreasing H2O2 in guard cells. Isolated epidermal strips of wild-type Arabidopsis were incubated at 25°C in either buffer (Control), or containing 10 μM ABA, 10 μM ABA + 0.5 mg L-1 ALA, 10 μM ABA + 100 μM AsA, 10 μM ABA + 100 U mL-1 CAT, 10 μM ABA + 10 μM DPI for 1 h under light (240 μmol m-2 s-1), respectively, and then images (C) were recorded and stomatal apertures (D) were determined. Images (C) were recorded by light microscopy (Nikon TE100, 400×), using a fitted camera (MShot Digital Imaging System). Scale bar: 10 μm. Values are the means of 90 measurements ± SE from three independent experiments. The same letters represent no significant differences between treatments (P < 0.01).
