FIGURE 6.
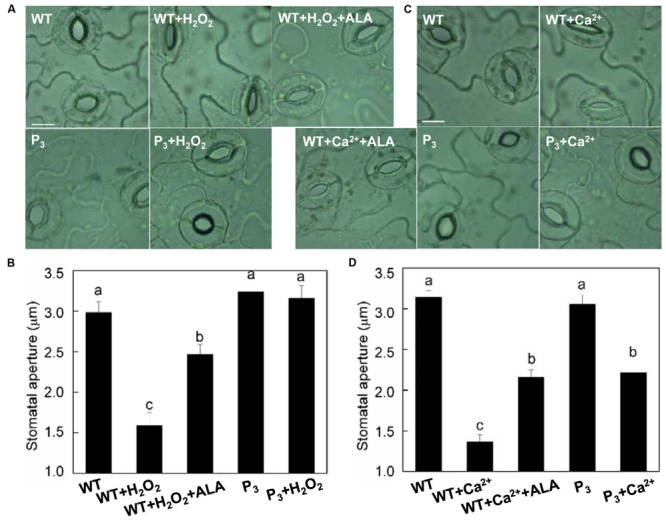
ALA inhibits H2O2- and Ca2+-induced stomatal closures. (A,B) ALA inhibits exogenous H2O2-induced stomatal closure. Isolated epidermal strips of wild-type Arabidopsis were incubated in either buffer alone or containing 200 μM H2O2, 200 μM H2O2 + 0.5 mg L-1 ALA, respectively, while P3 peels were incubated in either buffer or containing 200 μM H2O2 at 25°C under light (240 μmol m-2 s-1). One hour later, images (A) were recorded and stomatal apertures (B) were determined. (C,D) ALA inhibits exogenous Ca2+-induced stomatal closure. Isolated epidermal strips of wild-type Arabidopsis were incubated in either buffer alone or containing 2 mM CaCl2, 2 mM CaCl2 + 0.5 mg L-1 ALA, respectively, while P3 peels were incubated in either buffer or containing 2 mM CaCl2 at 25°C under light (240 μmol m-2 s-1). One hour later, images (C) were recorded and stomatal apertures (D) were determined. Images (A,C) were recorded by light microscopy (Nikon TE100, 400×), using a fitted camera (MShot Digital Imaging System). Scale bar: 10 μm. Values are the means of 90 measurements ± SE from three independent experiments. Different small letters represent significant difference between treatments (P < 0.01).
