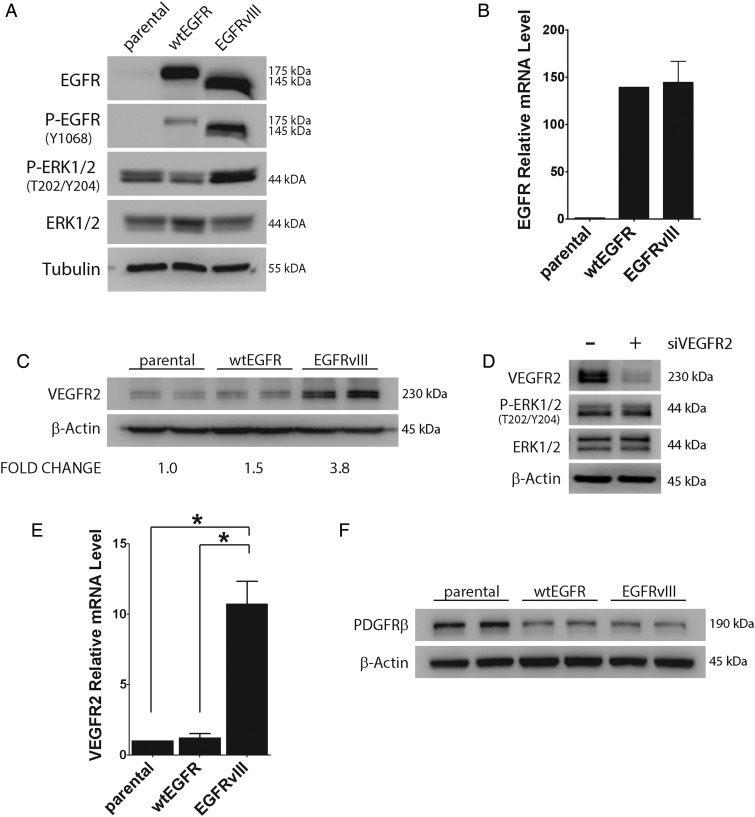
Fig. 2.
VEGFR2 is increased in EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG GBM cells. (A) Cell extracts from parental, wtEGFR-overexpressing, and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Blots were immunostained to detect tubulin as a loading control. (B) Total EGFR mRNA (wtEGFR + EGFRvIII) was determined by qPCR and standardized against the level present in parental cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3). (C) Immunoblot analysis to detect VEGFR2 was performed comparing parental, wtEGFR-overexpressing, and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells. Each cell type is shown in duplicate. VEGFR2 signal intensity was standardized against actin and shown relative to that measured in parental cells (n = 3). (D) EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were transfected with VEGFR2-specific (+) or NTC siRNA (−) for 24 h and subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect VEGFR2, phosphorylated ERK1/2 (P-ERK1/2), and total ERK1/2. (E) VEGFR2 mRNA was determined by qPCR and standardized against levels present in parental cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < .05). (F) Immunoblot analysis to detect PDGFRβ was performed comparing parental, wtEGFR-overexpressing, and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells (in duplicate).