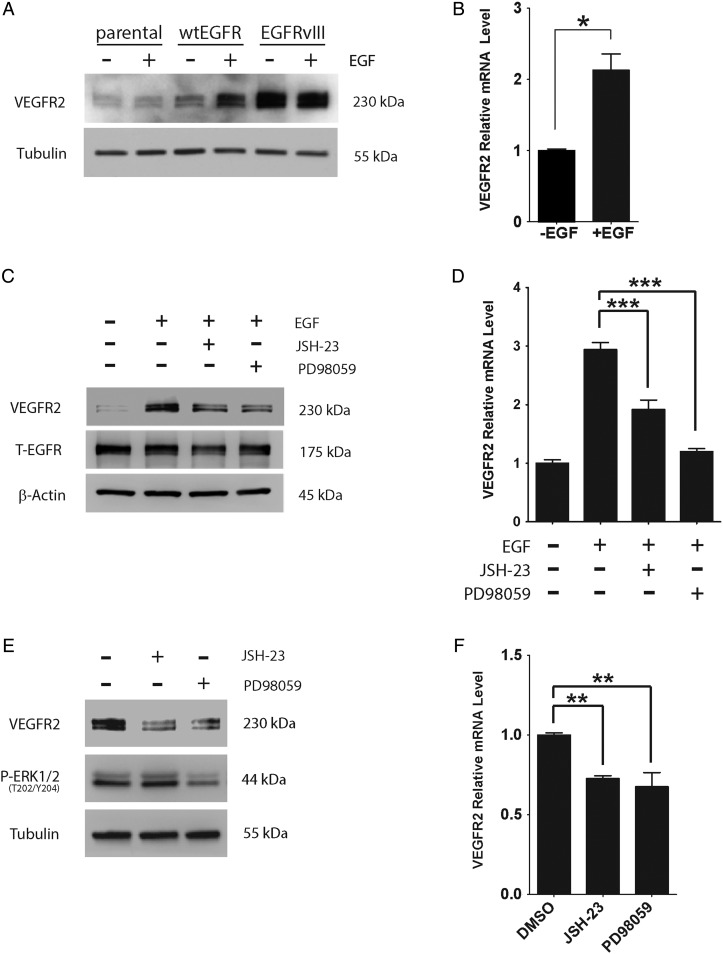
Fig. 4.
EGFR signaling to MEK and NFκB controls VEGFR2 expression in GBM cells. (A) Parental, wtEGFR-overexpressing, and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were serum starved for 18 h and then incubated with EGF (10 ng/mL) (+) or vehicle (−) for 6 h. Immunoblotting was performed to detect VEGFR2. (B) VEGFR2 mRNA levels were determined in wtEGFR-overexpressing U87MG cells treated with EGF (+) or vehicle (−) by qPCR and standardized against vehicle-treated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < .05). (C) WtEGFR-overexpressing U373MG cells were serum starved for 18 h and then pretreated for 15 min with either JSH-23 (10 µM), PD98059 (50 µM), or vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]). The cells were subsequently treated with EGF (10 ng/mL) (+) or vehicle (−) for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect EGFR and VEGFR2. T-EGFR = Total not truncated EGFR. (D) WtEGFR-overexpressing U373MG cells were serum starved for 18 h and pretreated for 15 min with either JSH-23 (10 µM), PD98059 (50 µM), or vehicle and then treated with EGF (10 ng/mL) (+) or vehicle (−) for 6 h. VEGFR2 mRNA was determined by qPCR (mean ± SEM, n = 4, ***P < .001). (E) EGFRvIII-expressing U373MG cells were serum starved for 18 h and treated with either JSH-23 (10 µM), PD98059 (50 µM), or vehicle for 6 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect VEGFR2, phospho-ERK1/2 (P-ERK1/2), and tubulin as a control for load. (F) EGFRvIII-expressing U373MG cells were serum starved for 18 h and treated with either JSH-23 (10 µM), PD98059 (50 µM), or vehicle (DMSO) for 6 h. VEGFR2 mRNA was determined by qPCR and standardized against the level present in vehicle-treated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 5, **P < .01).