Figure 7. Catalytic role of HCl during hydrolysis and condensation processes.
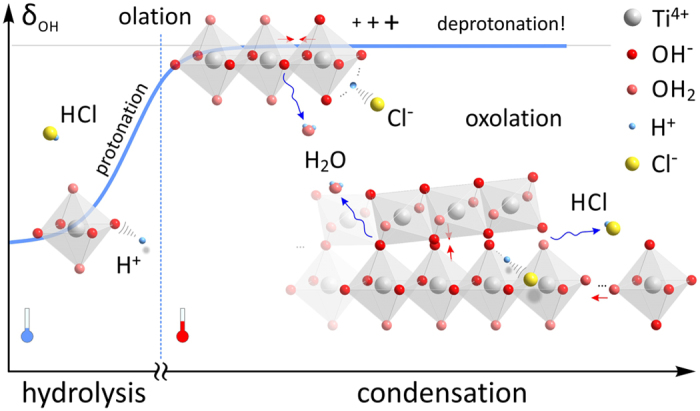
In acidic medium, HCl protonates OH− ligands in Ti(IV)-complexes, making them stable at ambient conditions. At elevated temperatures the hydroxo-aquo complexes loose water through associative nucleophilic reactions to form chains of Ti-octahedra (olation). With their length charge increases to the point when free Cl− ions can trap migrating protons and deprotonate growing polycondensate, allowing further release of water (oxolation) and their assembly into the rutile structure.
