FIG. 2.
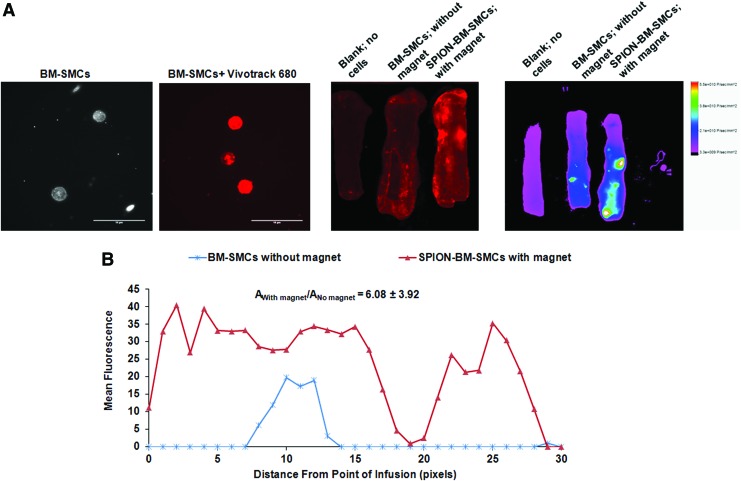
SPION-labeling of BM-SMCs in conjunction with an applied magnetic field significantly increases uptake and retention of the cells into matrix-disrupted porcine carotids upon ex vivo infusion. Representative images show successful BM-SMC labeling with infrared emitting fluorescent tracker dye (Vivotrack 680), (A) distribution of Vivotrack 680-labeled BM-SMCs (without magnet) or SPION-BM-SMCs (with magnet) within porcine carotid arteries as viewed using an Odyssey scanning system, (B) and a Bruker whole tissue imaging system (C). Quantitative analysis (D) of whole tissue image (C) showing the mean fluorescence intensities in carotids with BM-SMCs or SPION-BM-SMCs corrected for background relative to carotid with no cells (blank). Fold differences in area under the curves represented as mean ± SD values from n = 3 carotids/case indicate significant retention of SPION-BM-SMCs in presence of magnet compared to BM-SMCs without magnet. Scale bars = 10 μm. SD, standard deviation. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tec