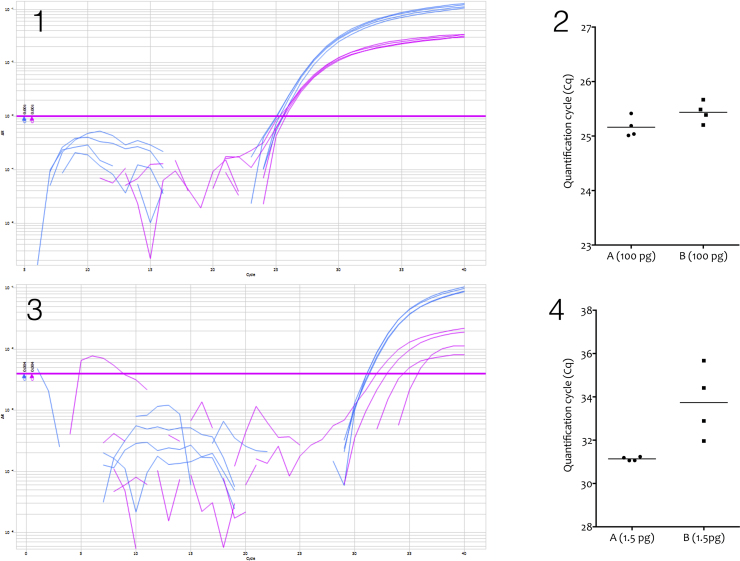
Fig. 1.
Comparison of a dualplex qPCR assay targeting Candida dublinensis or Candida glabrata. (1) A PCRmax Eco (http://www.pcrmax.com) was used to amplify 100 pg of C. glabrata (A) and C. dublinensis (B) and DNA. Four replicate reactions were run of 5 μl each using Agilents’s Brilliant III qPCR mastermix, with PCR amplicons detected using FAM-(C. glabrata, A, blue)- or HEX-(C. dublinensis, B, pink) labelled hydrolysis probes. The assays are 98% and 97% efficient, respectively. (2) Plots of the two assays recording average Cqs of 25.16 ± 0.19 and 25.44 ± 0.19 for C. glabrata and C. dublinensis, respectively (Mean ± SD). (3) Conditions as described for 1, except that the replicates contained 1.5 pg of each of the fungal DNAs. (4) Plot of the two assays recording average Cqs of 31.14 ± 0.09 and 33.73 ± 1.64 for C. glabrata and C. dublinensis, respectively (Mean ± SD).