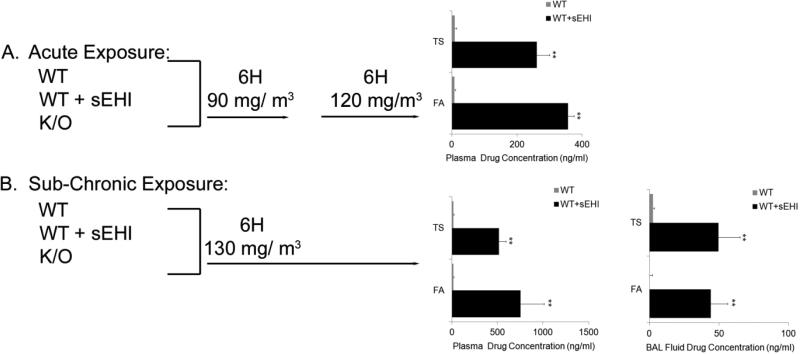
Figure 2. An overview of the study design with the acute (A) and sub-chronic (B) tobacco smoke exposure models (two days and one month exposure, respectively).
In the acute model, wild-type (WT), WT treated with inhibitor (WT + sEHI) and their knock-out (K/O) counterparts were exposed to filtered air (FA) or tobacco smoke (TS) for 6 hours/day at 90 and 120 mg/m3. In the sub-chronic model, WT, WT + sEHI and K/O were exposed to FA or TS for 6 hours/day at 130 mg/ m3. Plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid concentrations of the sEH inhibitor 1-(1-methylsulfonyl-piperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-urea (TUPS) in WT mice exposed to FA or TS for two days and one month are shown in black bars (no treatment of K/O animals), and the limit of quantification are shown for non-treated WT mice (grey bars). Data are presented as mean ± SE. **P < 0.001 (n=6), significant differences between drug levels in non-treated WT mice and WT mice treated with TUPS.