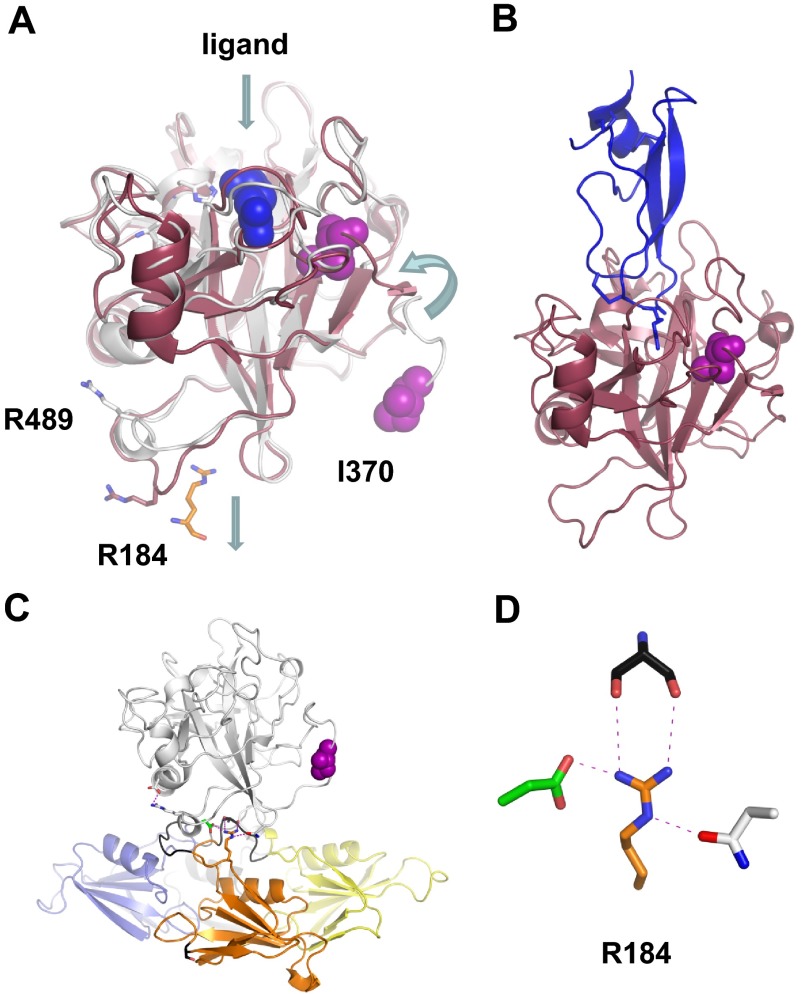
Figure 6.
The FXIa protease domain. (A) Topologic diagram showing the superposition of FXI (white) and FXIa (red) protease domain crystal structures. Conformational changes include a 12 Å shift in the position of Ile370 into the protease core after cleavage of the Arg369-Ile370 bond, and an unraveling of an α-helix containing Arg489 to fill a pocket left empty by removal of the A3 domain and Arg184. The Arg side chain from the FXIa ligand in panel B is shown in blue. (B) Structure of FXIa in complex with PN2-KPI domain inhibitor (blue). (C) The side chain of Arg184 is buried in the FXI zymogen through contacts with the protease domain. This residue is thought to act as a switch, which is released on zymogen activation to engage substrate FIX. (D) Stick diagram showing the side chain of Arg184 that forms 3 noncovalent interactions with the side chains of Ser268 (gray) from the A3 domain, and Asp488 (green) and Asn566 (white) from the protease domain in the FXI zymogen structure.