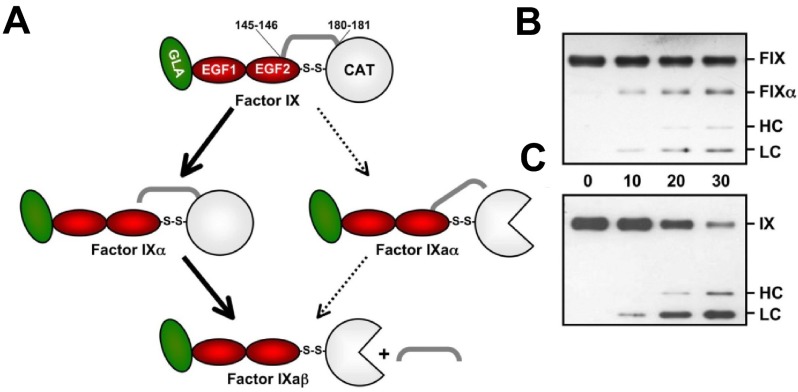
Figure 7.
FIX activation. (A) FIX contains (from the N-terminus) a Gla domain (green), 2 epidermal growth factor (EGF) domains (red), an activation peptide (AP; gray bar), and a catalytic (CAT) domain (white). FIX is converted to FIXaβ by cleavage after Arg145 and Arg180, releasing the AP. FVIIa/TF initially cleaves FIX after Arg145 to form the intermediate FIXα, with subsequent cleavage after Arg180 to form FIXaβ (bold arrows). White three-fourths circle represents the active catalytic domain of FIXaβ. During this reaction, FIXα accumulates before formation of FIXaβ. FXIa also cleaves FIX initially after Arg145; however, no FIXα accumulates. Initial cleavage of zymogen FIX after Arg180 to generate the intermediate FIXaα appears to be a minor reaction (thin arrows). (B-C) Reducing Western blots of FIX (100nM) activated by 1nM FVIIa/TF (B) or FXIa (C) over 30 minutes (time indicated between panels). Markers at the right indicate migration of standards for zymogen FIX (FIX), the large fragment of FIXα (FIXα), the heavy chain (HC) of FIXaβ, and the light chain (LC) of FIXα or FIXaβ. No FIXα accumulates during activation by FXIa.